

Recently formed partnerships are revealing the urgency of carmakers in the race to secure stable supplies for electric vehicles (EVs) and their ambitions to break into the Chinese market. Toyota and Volkswagen, the world's two largest carmakers, have both announced electric vehicle battery partnerships with Chinese manufacturers this month.
Sourcing from a Chinese company for the first time, Toyota agreed to buy batteries from Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL) as part of a broader partnership. According to a statement released by Toyota, the two companies also discussed teaming up in battery recycling technology. Toyota has also agreed to jointly develop batteries with BYD, one of China's biggest EV brands. These partnerships are all set to contribute to fast-forwarding Toyota's target of electrifying half of its delivery by 2025.
Volkswagen announced earlier this month that it will buy 50 billion euros' (56.57 billion U.S. dollars) worth of battery cells and identified CATL as one of its partner. It plans to start producing 33 different electric cars by mid-2023.

VCG Photo
Driven by a global push to reduce greenhouse gases, carmakers around the world are increasing the number of electric vehicles in their line-ups to meet stricter emissions rules. Increased demand is fueling fierce competition in the race to secure supplies of high quality, durable batteries.
Top suppliers
China is at the top when it comes to EV battery manufacturing. Chinese makers are expected to claim three of the top five slots on the list of the world's largest EV battery producers in 2021, according to Bloomberg New Energy Finance. The research organization also projects that China will produce 70 percent of the world's EV batteries by 2021.
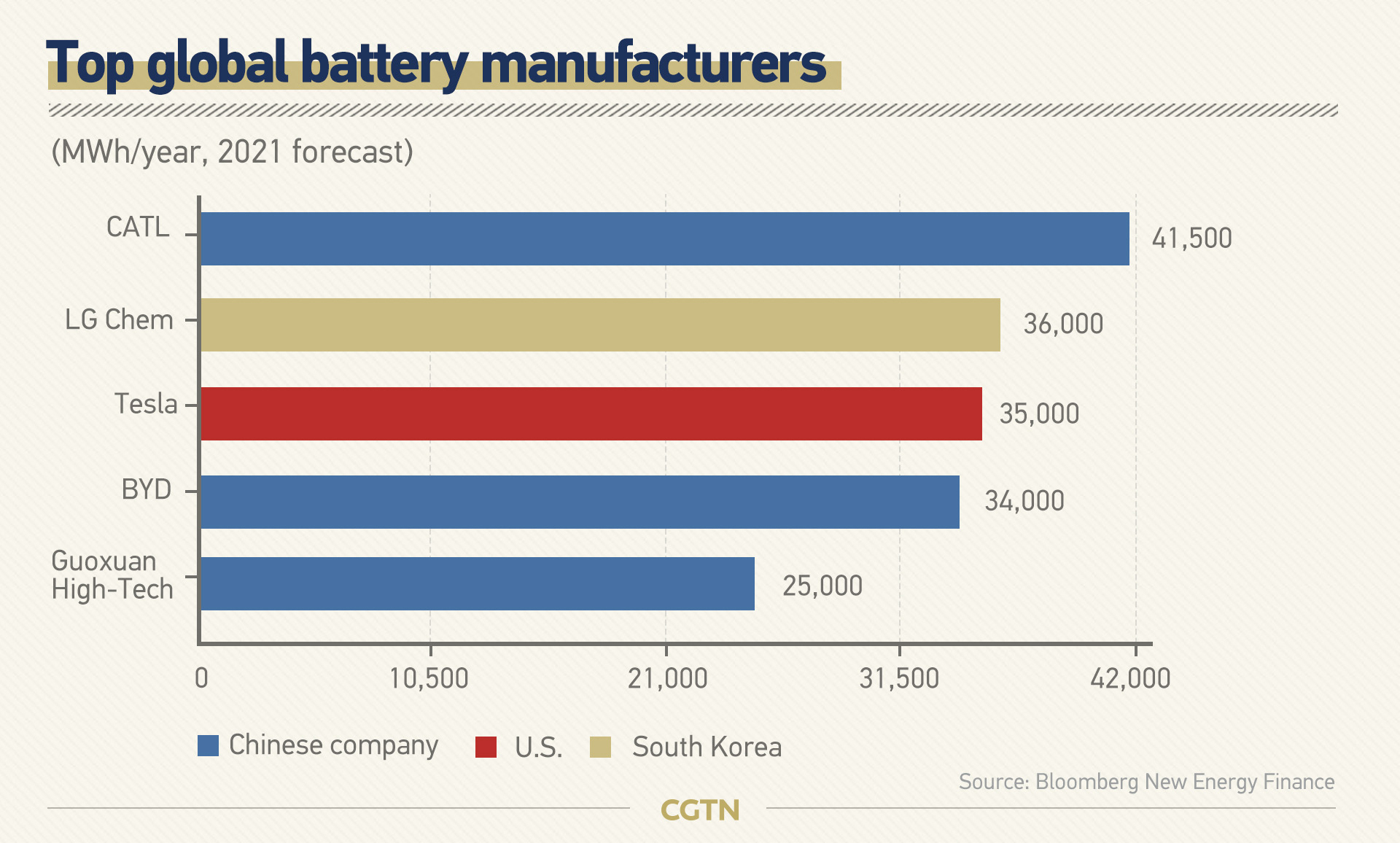
Founded in 2011, CATL overtook Panasonic as the world's largest supplier of EV batteries in terms of sales in 2017. Data from Bloomberg New Energy Finance shows that batteries account for 33 percent of the total cost of an EV in 2019. In 2017, they accounted for around half of the total cost. Although batteries are getting cheaper to produce, Goldman Sachs estimates that sales of batteries will rise to 60 billion U.S. dollars by 2030.
China's EV market
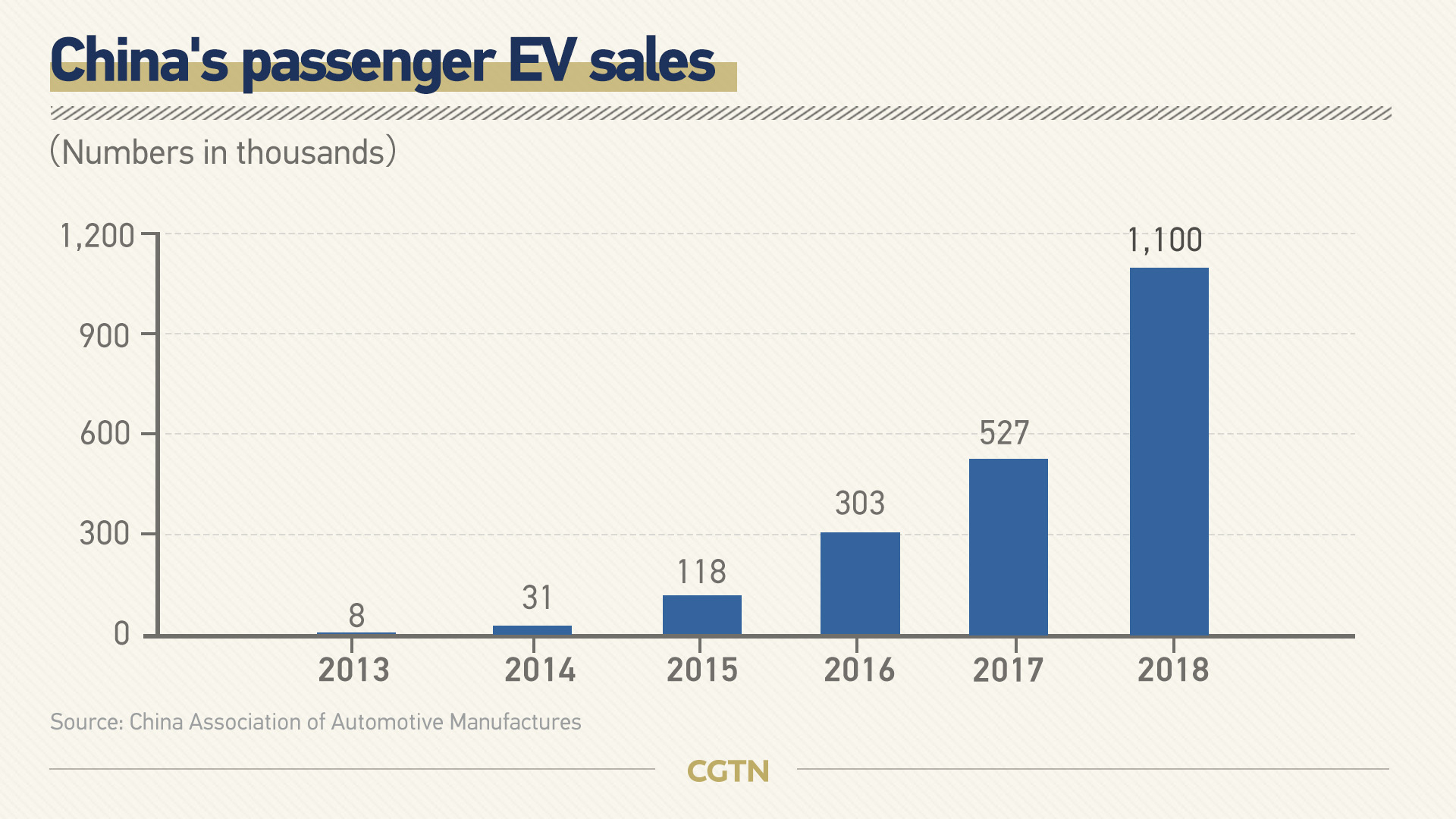
China is already the world's largest market for electric vehicles, and the country's EV sector has expanded strongly, with sales surging to more than 1.1 million units by the end of 2018. The annual growth rate registered at 118 percent between 2011 and 2018.
In the first half of 2019, a total of 617,000 units were sold in China, representing year-on-year growth of 49.6 percent.
Read more: China builds world's largest network of charging stations for electric vehicles
The International Energy Agency estimates that the global EV market will be worth 570 billion U.S. dollars by 2025, with China making up for 60 percent of market share. The agency also predicted global EV sales will reach 23 million in 2030.
Policy change fuels competition
China's EV industry is expecting intensified competition amid a background of shrinking subsidies. The country has been cutting subsidies for the EV sector since 2017, with all support expected to be completely scrapped by 2020.
In addition, a list for "recommended battery suppliers" was scrapped in June. The list was first published in 2015 to provide subsidies for recommended domestic companies.
China removed equity caps on foreign carmakers in the EV and plug-in hybrids sectors in 2018. Besides, caps on commercial vehicle makers will be eased in 2020 and by 2022 for the wider car market.
These policies open up the world's biggest market for electric vehicle batteries and at the same time add pressure on domestic producers.
Toyota aims to launch 10 new electric models by 2025, including electric sedans and low-floor SUVs. The carmaker plans to ramp up production of EVs in China, expanding capacity at a Chinese plant run with its joint-venture partner Guangzhou Automobile Group to as much as 400,000 vehicles a year by 2022, Nikkei reported.

Copyright © 2018 CGTN. Beijing ICP prepared NO.16065310-3
Copyright © 2018 CGTN. Beijing ICP prepared NO.16065310-3