

China on Tuesday released a white paper on the country's nuclear safety, reaffirming its commitment to the safe, sound and sustainable development of its nuclear industry.
The white paper, published by the State Council Information Office (SCIO), is the first comprehensive one that details China's approach to nuclear safety.
At a press conference presenting the white paper, Liu Hua, China's vice minister of Ecology and Environment and director of the National Nuclear Safety Administration, said China has always regarded nuclear safety as an important responsibility and maintained a good record in the area.

The white paper titled "Nuclear Safety in China" is released by the State Council Information Office (SCIO) on September 3, 2019. /Photo via SCIO
China's good nuclear safety record
China ranked among the highest of all countries in terms of nuclear power safety operation indicators, and its nuclear industry has always developed in line with the latest safety standards, the white paper said.
The country's safety level in the use of nuclear technology continues to improve, its nuclear material control is strong, and public health and environmental safety are fully guaranteed.
In 2000, 2004, 2010 and 2016, the International Atomic Energy Agency conducted four comprehensive reviews of China's nuclear and radiation regulation, giving full recognition to China's good practices and experiences.
By June 2019, China had 47 nuclear power units in operation, ranking third in the world, and 11 nuclear power units under construction, ranking first in the world.
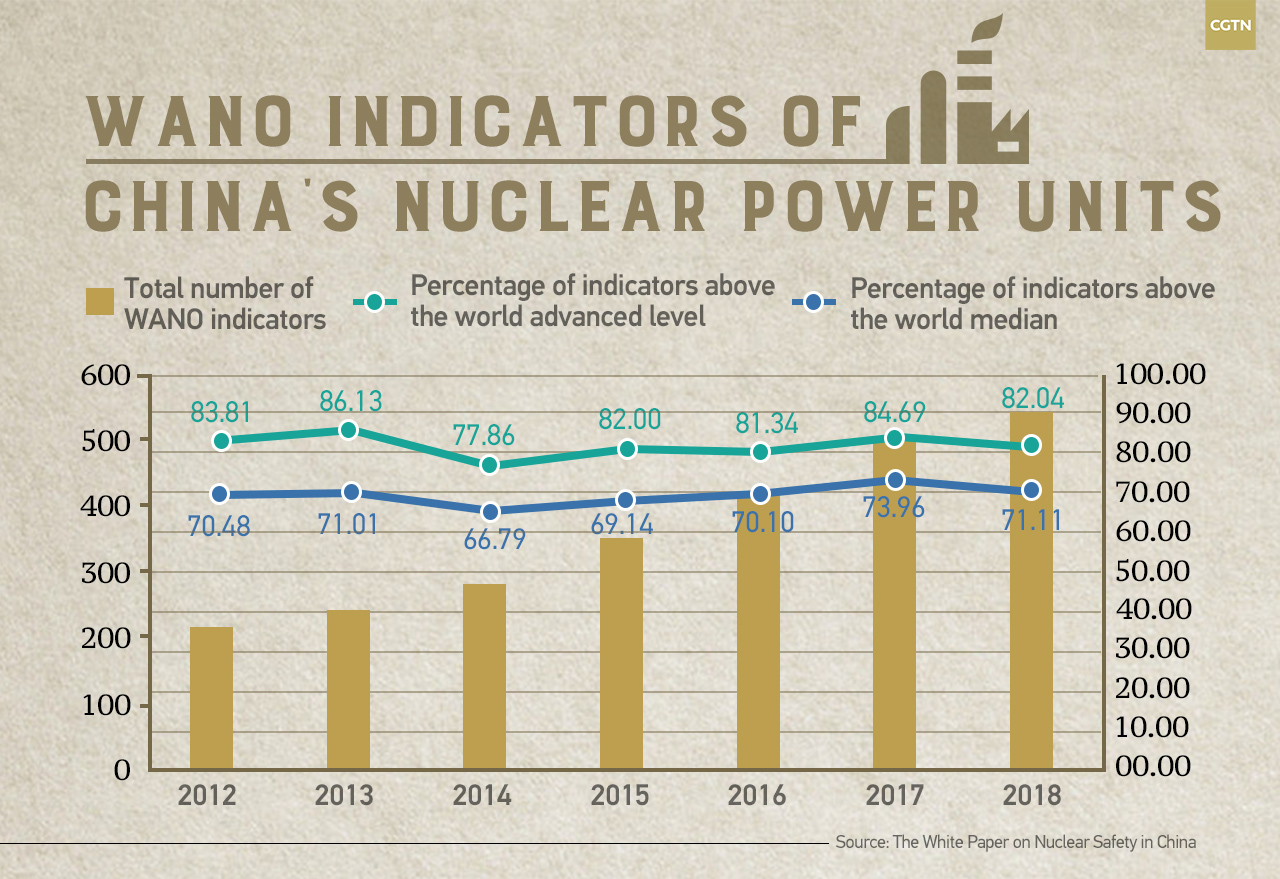
CGTN Infographic by Yin Yating
According to recent rankings by the World Association of Nuclear Operators (WANO), more than 80 percent of safety indicators from Chinese nuclear power facilities have surpassed the world's average, and more than 70 percent of these indicators have reached world-class level, according to the white paper.
In 2018, China led the world with 12 operating units achieving full marks in the WANO composite index, according to the white paper.
Equal emphasis on development and safety
China will place equal emphasis on development and safety, and develop the nuclear industry in a context of guaranteed safety, the white paper said.

CGTN Infographic by Yin Yating
Although there is a tendency of denuclearization in some countries after the nuclear incident in Japan's Fukushima in 2011, China chooses to continue the development of nuclear power in order to better protect the environment.
"China's coal-based energy structure has determined that we must develop clean and efficient energy," Liu said when answering question from the media, adding that clean energy is essential for environmental protection.

Liu Hua, China's vice minister of Ecology and Environment and director of the National Nuclear Safety Administration attends the press conference, September 3, 2019. /Photo via SCIO
In the wake of the Fukushima nuclear accident, the Chinese government organized a nine-month safety inspection of the country's operating nuclear power plants, those under construction, research reactors, and other key nuclear facilities.
China has also been ensuring nuclear safety through round-the-clock radiation environment monitoring.
The country has established a three-tier radiation environment monitoring system at state, provincial and municipal levels.
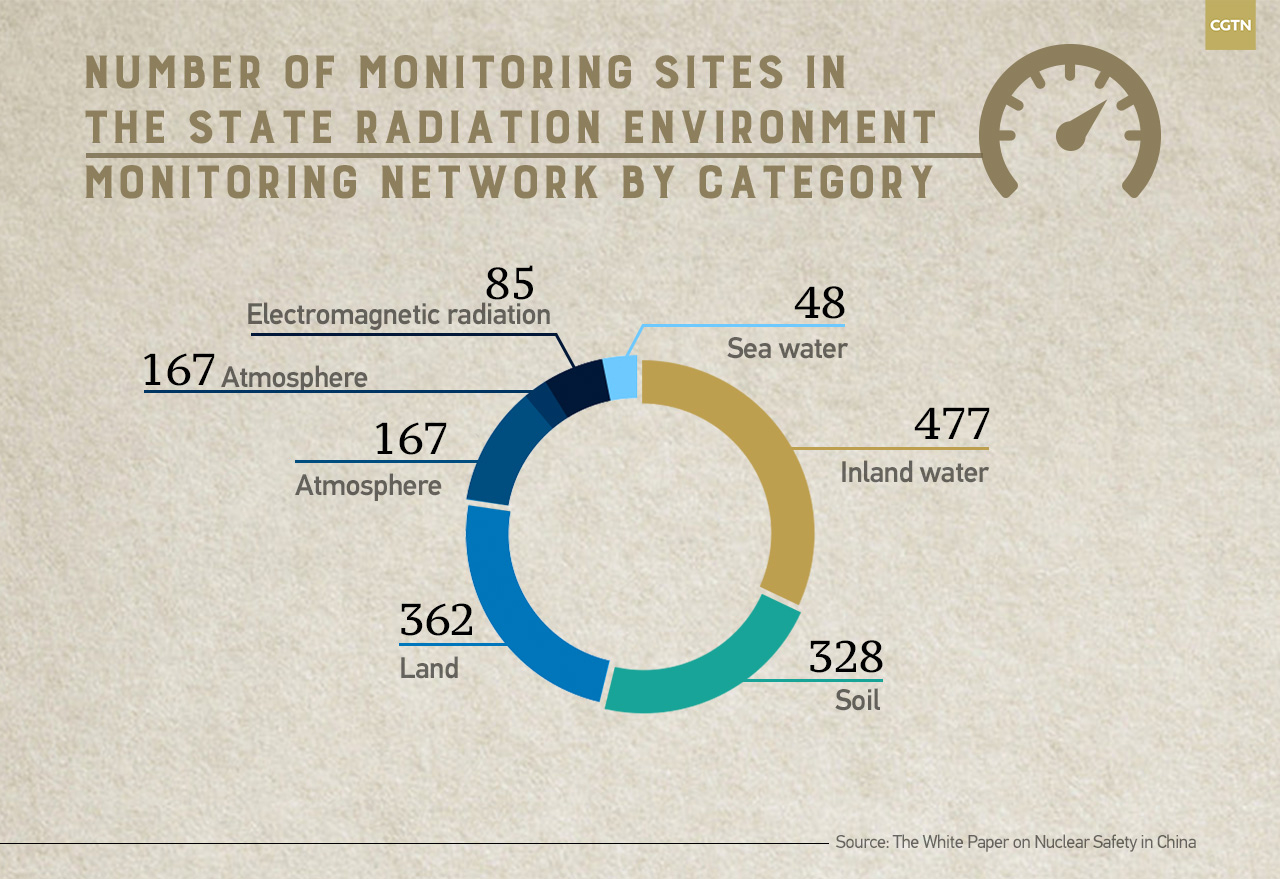
CGTN Infographic by Yin Yating
The state radiation environment monitoring network had 1,501 monitoring sites as of this June, which consists of 167 automatic monitoring sites for atmospheric radiation, 328 land sites, 362 soil sites, 477 inland water sites, 48 seawater sites, 85 electromagnetic radiation sites, and 34 marine life sites.
There were also 46 radiation environment surveillance monitoring systems set up in the vicinity of key nuclear facilities as well as sites set up to monitor radioactivity in food, said the white paper.
China-U.S. trade frictions
In August, the U.S. blacklisted the major Chinese nuclear company, China General Nuclear Power Group, and three of its subsidiaries, barring U.S. companies from supplying components and technology to them without obtaining licenses.
During the press conference, Liu was asked whether the U.S. restrictions would affect China's nuclear development and safety.
Liu said that the U.S. abused its export control measures, which would not only harm Chinese companies, but also their U.S. counterparts.
He said cooperation in nuclear development over the past 35 years between the two countries has been mutually beneficial and fruitful, which has promoted the improvement of nuclear safety levels in both countries.
But the U.S. is not the only partner of China in nuclear energy development, he said. China has also been collaborating with France and Russia and has made substantial progress.
"The global market for nuclear cooperation is vast," Liu said.
(CGTN's Lu Sirui also contributed to the story.)

Copyright © 2018 CGTN. Beijing ICP prepared NO.16065310-3
Copyright © 2018 CGTN. Beijing ICP prepared NO.16065310-3