04:07
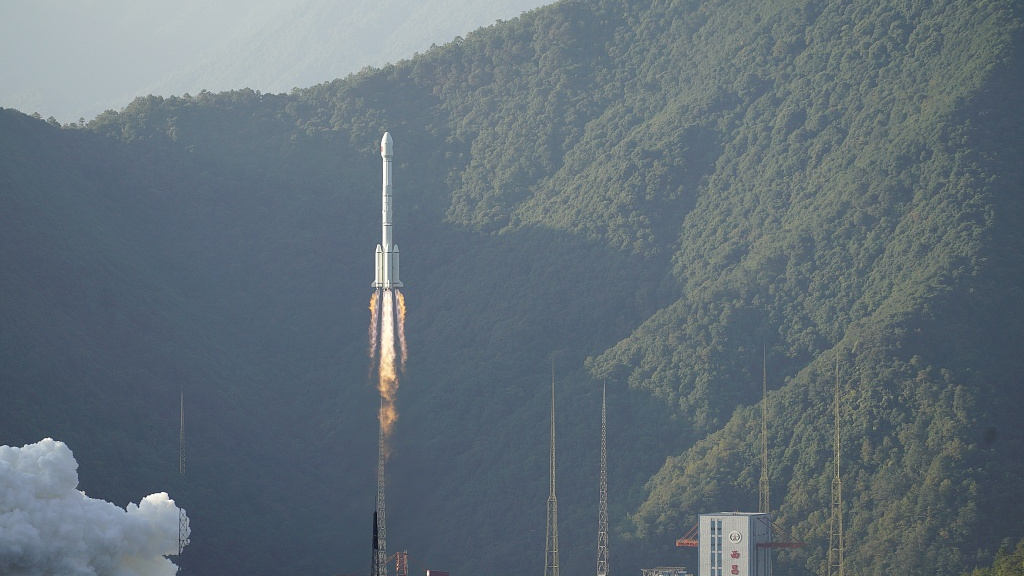

Twenty-four medium earth orbit (MEO) satellites will all be sent to their designated orbits to form the core part of China's BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) constellation by the end of this year, Yang Changfeng, chief designer of the BDS said at the 14th session of the international committee on global satellite navigation systems (ICG) in Bangalore, India, on Monday.
"Currently, the positioning accuracy of the BDS has reached 2.6 meters in the Asia-Pacific region and 3.6 meters globally," said Yang. "In the future, it will be embedded in mobile phones to achieve centimeter-level positioning accuracy."
China started developing its satellite navigation system in the last century. The BDS-1 system was completed by the end of 2000, designed to offer services domestically. The updated version BDS-2, which expanded the service range to Asia-Pacific regions, was finished by 2012. The latest BDS-3, targeting global users, is the third stage of the plan, functioning as the U.S.' GPS, Russian GLONASS and European Galileo systems.
04:28
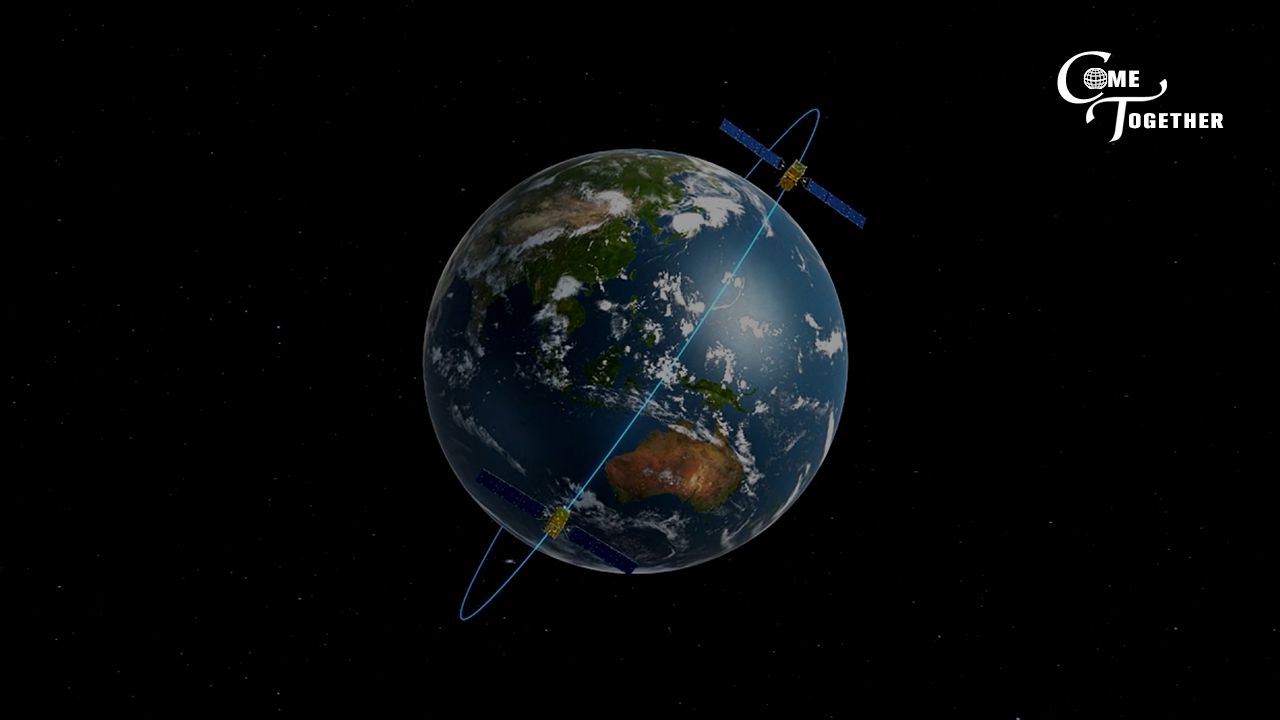
The BDS-3 constellation featured 24 satellites on MEO, three in a geostationary Earth orbit, and three in an inclined geosynchronous Earth orbit.
Unlike the U.S.' GPS, whose satellites all fly in MEO at an altitude of approximately 20,200 kilometers and whose control segment consists of a global network of ground facilities, BDS has a mixed constellation with satellites that travel at both high and medium altitude.
The reason for building a mixed constellation is due to the topography limitation. BDS has to be tracked, monitored and commanded within the Chinese territory, Yang Hui, chief designer of the BDS-2 project, explained.
In the meantime, satellites in high orbits can offer better anti-shielding capabilities. They also provide navigation signals on multiple frequencies to improve service accuracy by using combined multi-frequency signals.
According to the China Satellite Navigation Office, by 2035 a more ubiquitous, integrated and smarter positioned navigation and timing (PNT) BDS system will be put in place.
With 5G technology now in commercial use, the "5G+BDS" combo will be widely applied in scenarios that require fast data transmission speed, low network latency, as well as precise location and navigation services.
For example, BDS helps mariners to navigate, measure speed and determine location. Commercial fishing fleets can map out optimum fishing locations and track fish migrations based on the navigation. It can be installed in driverless tractors for high-accuracy sowing to maximize farmland utilization and increase crop yields in agriculture. The BDS logistic system is able to achieve lane-level navigation and provide live updates.
(CGTN's Ning Hong also contributed to the story)