Editor's Note: Jimmy Zhu is a chief strategist at Fullerton Research. The article reflects the author's opinion, and not necessarily the views of CGTN.
The announcement by People's Bank of China (PBOC) on easing the liquidity on the first day of the year signals the monetary policy will be more growth-oriented in 2020, instead of just for coping with the seasonal cash demand as many PBOC's watchers thought.
Chinese central bank announced to reduce the required reserve ratio (RRR) by 50 basis points (bps) for commercial banks on January 1, and the effective day will start from January 6. The cut is expected to release over 800 billion yuan of liquidity in the banking system. The central bank cut the RRR by 150 bps to 13 percent for major banks in 2019.
The cut is widely expected as the cash demand for this month will be particularly high. PBOC usually injected over 600 billion yuan in recent years before the Chinese New Year to smooth the liquidity condition, and the amount of upcoming corporate tax payment in late January will be around 500 billion yuan. The "one-time" cash demand would be easily above 1 trillion yuan for this month.
Seasonal overwhelming cash demand was attributed to the RRR cut by many PBOC watchers, but a chart below shows PBOC seldom reduced the RRR in the month of Lunar New Year in the past decade, except for 2015 and 2019. If the central bank only aims to inject liquidity into the banking system to avoid a liquidity crunch, it can be done through open market operations (OMO) or other credit facilities such as medium-term lending facility (MLF), not necessary from a toolkit that permanently releases liquidity.
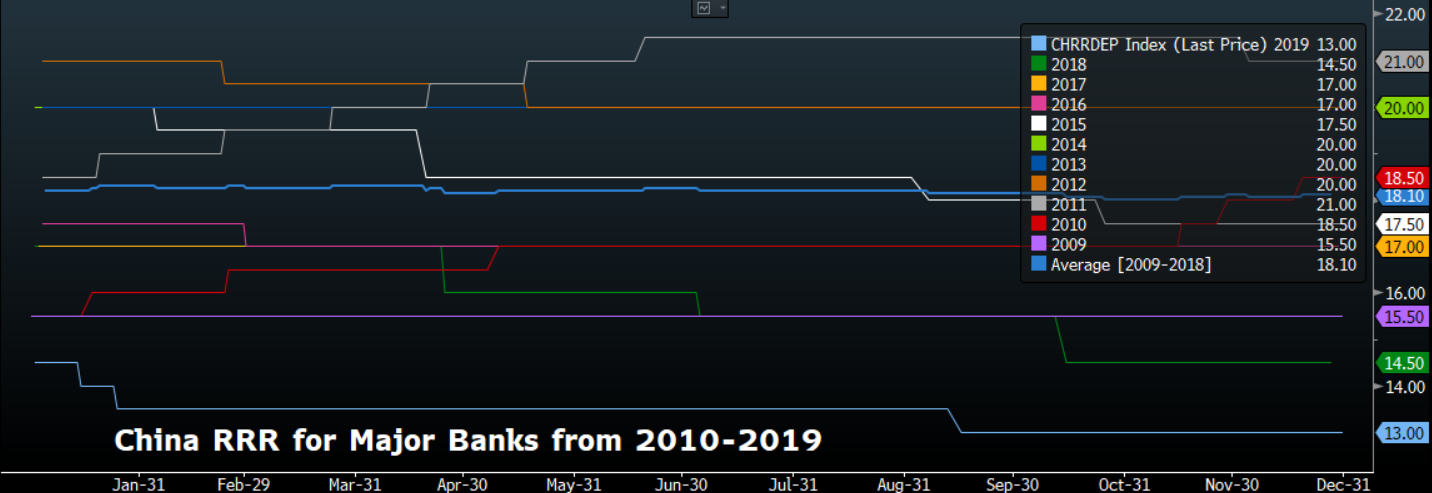
Looking back into those two RRR cuts in February 2015 and January 2019, the reasons behind were more than countering the seasonal cash demand. Both were unexpected considering the timing or size of the cuts. For the first one, it occurred in the period when yuan outflows increased and factory activities slowed down. The PBOC had been injecting the liquidity by reducing the RRR throughout 2015. It paused the easing in RRR when capital outflows moderated at the beginning of 2016. For the second one, it happened in the background when policymakers pledged to ease the funding difficulties for private sectors.
For this round, PBOC announcing the RRR cut on the first day of 2020 may reflect its upcoming policy stance could be towards growth-oriented. When the global central banks were busy with cutting the benchmark policy rates to counter the recession fears last year, PBOC's monetary policy wasn't very pro-active compared to its peers from the federal reserve to India's central bank.
PBOC's quiet measures in 2019 suggest it may have a bigger room for monetary easing this year, and bond markets express the same opinion. Spread between China and the U.S., 10-year government bond yield widened by around 70 bps in 2019, now standing at 122 bps. PBOC's Governor Yi Gang mentioned in 2018 that a comfortable gap between the two countries' yield would be around 80-100 bps, so the current spread offers China further room to act more dovish than many other major central banks.
One of the restrains for PBOC to ease the monetary policy last year was the rising pork prices, a key component that stoked inflation. After China implemented various measures to increase the supply of pork in recent months, the pork wholesale spot price dropped 16 percent from November's peak level, according to data from the Ministry of Commerce.
Declines in pork prices in December are likely to slow the CPI growth in this period, which will be released on January 9. If the data shows the CPI growth to fall below 4 percent for December, PBOC may further cut the new benchmark lending rate – one year Loan Prime Rate (LPR) – by another 5 bps on January 20.
Small-sized companies' funding condition remains challenging
The announcement of the RRR cut may also show officials' determination to offer more credit support to the domestic SMEs. Data released a few days ago shows the gap between the large-size and small-size companies' manufacturing PMIs sharply widened by 190 percentage points to 3.4. Part of the reasons behind this could be due to tougher funding conditions for small businesses. In early 2015, 2018 and 2019, the PMIs' spread between large and small companies also widened, and PBOC reduced the RRR thereafter in all those three occasions.
Shibor three-month rates, one of the key interbank lending rates, now climb above 3 percent, near the highest levels in the past 12 months. Unlike those large companies that can fund the cash through equities and bond markets, the small business' funding condition is usually more sensitive to the interbank lending rate, given their main channel to receive the credit is through banks' lending. Thus, the upward pressures in short-term money market rates may ease in the coming weeks or months.