Aimed at global coordination, solidarity and cooperation, the 15th Group of Twenty (G20) Summit will be held on Saturday and Sunday in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, to be attended by leaders from major countries and international organizations.
Accounting for around 90 percent of global GDP, G20 comprises the world's largest advanced and emerging economies. It is leading the global response and international collaboration against the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, the worst global crisis since the end of the Cold War.
According to a statement by host Saudi Arabia, G20 members have contributed over $21 billion to support the production, distribution and access to diagnostics, therapeutics and vaccines.

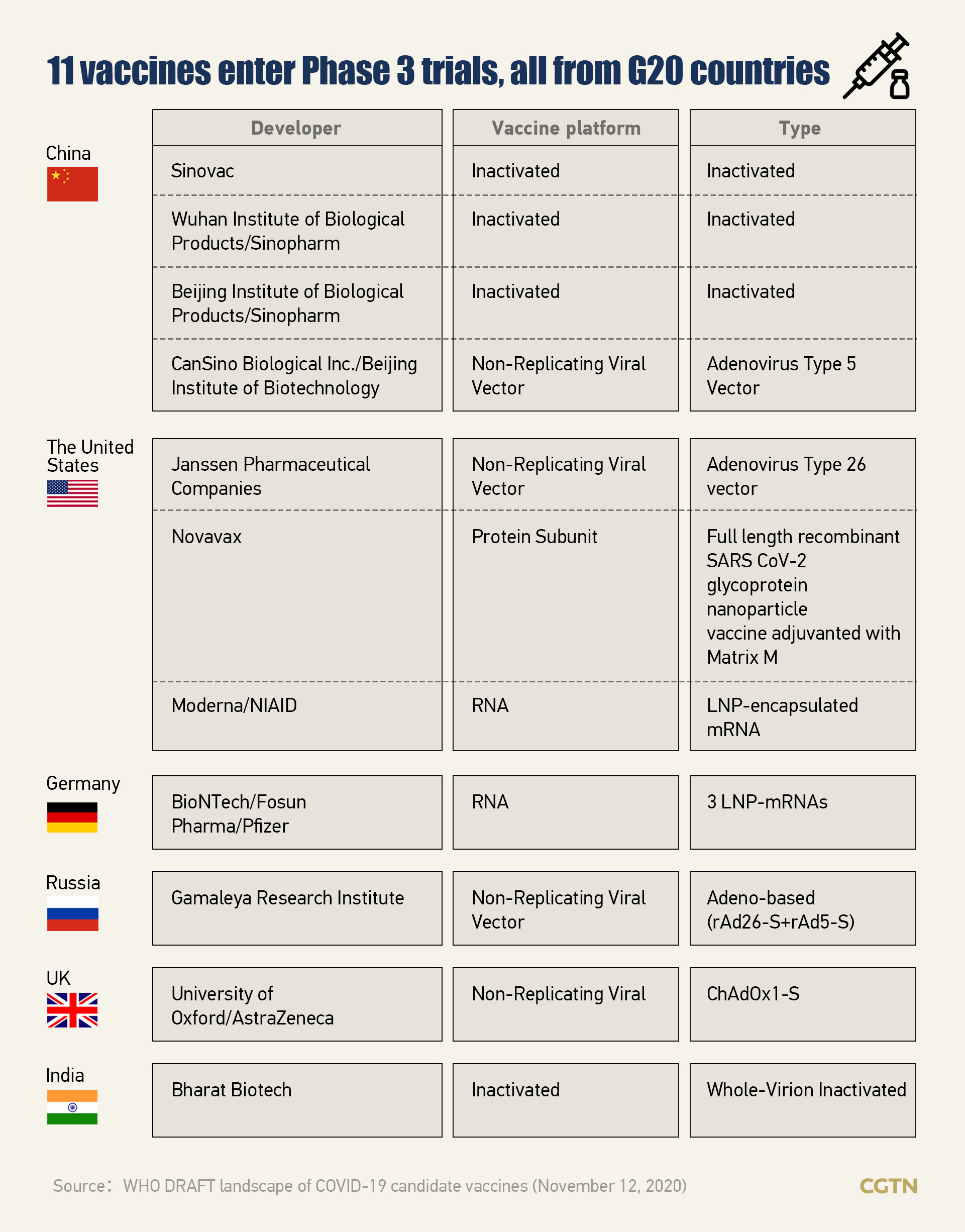
As the COVID-19 pandemic continue raging across the globe, thousands of scientists worldwide are making all-out efforts to create vaccines against the novel coronavirus. Statistics show that G20 countries lead the race for a COVID-19 vaccine.
As of November 12, the World Health Organization (WHO) had posted a list of 48 COVID-19 candidate vaccines in clinical evaluation – more than 90 percent developed by G20 countries – as well as 164 ones in pre-clinical evaluation on its site.
Among the 48 vaccines currently under clinical evaluation, 11 have entered phase-3 clinical trials, all of them from G20 countries. China and the U.S. are at the forefront, while the UK, Russia, Germany and India are also in the race.
In April, the WHO, the European Commission and multiple other partners launched "The Access to COVID-19 Tools (ACT) Accelerator" to catalyze the development and equitable distribution of vaccines, diagnostics and therapeutics.
The launch of the ACT Accelerator was welcomed by Saudi Arabia. G20 members including China, Saudi Arabia, Japan, UK and Brazil joined the COVAX Facility, one of the three pillars of the ACT Accelerator, to promote rapid, fair and equitable access to COVID-19 vaccines.
Since the COVID-19 outbreak, G20 members have united and cooperated to mount a collective response.
On March 26, the G20 held an emergency virtual summit, further committing to work together to increase research and development funding for vaccines and medicines, leverage digital technologies, and strengthen scientific international cooperation.
On April 15, G20 finance ministers and central bank governors approved the Debt Service Suspension Initiative to help the world's poorest countries cope with the fallout of the COVID-19 crisis.
On June 4, the UK-hosted Global Vaccine Summit, joined by some of the G20 including China, Germany, Japan and France, pledged 8.8 billion U.S. dollars for GAVI, the Vaccine Alliance to ensure vaccine accessibility worldwide.
On July 22, the G20 economic ministers adopted a declaration, emphasizing the role of connectivity, digital technologies, and policies in accelerating G20's collaboration and response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
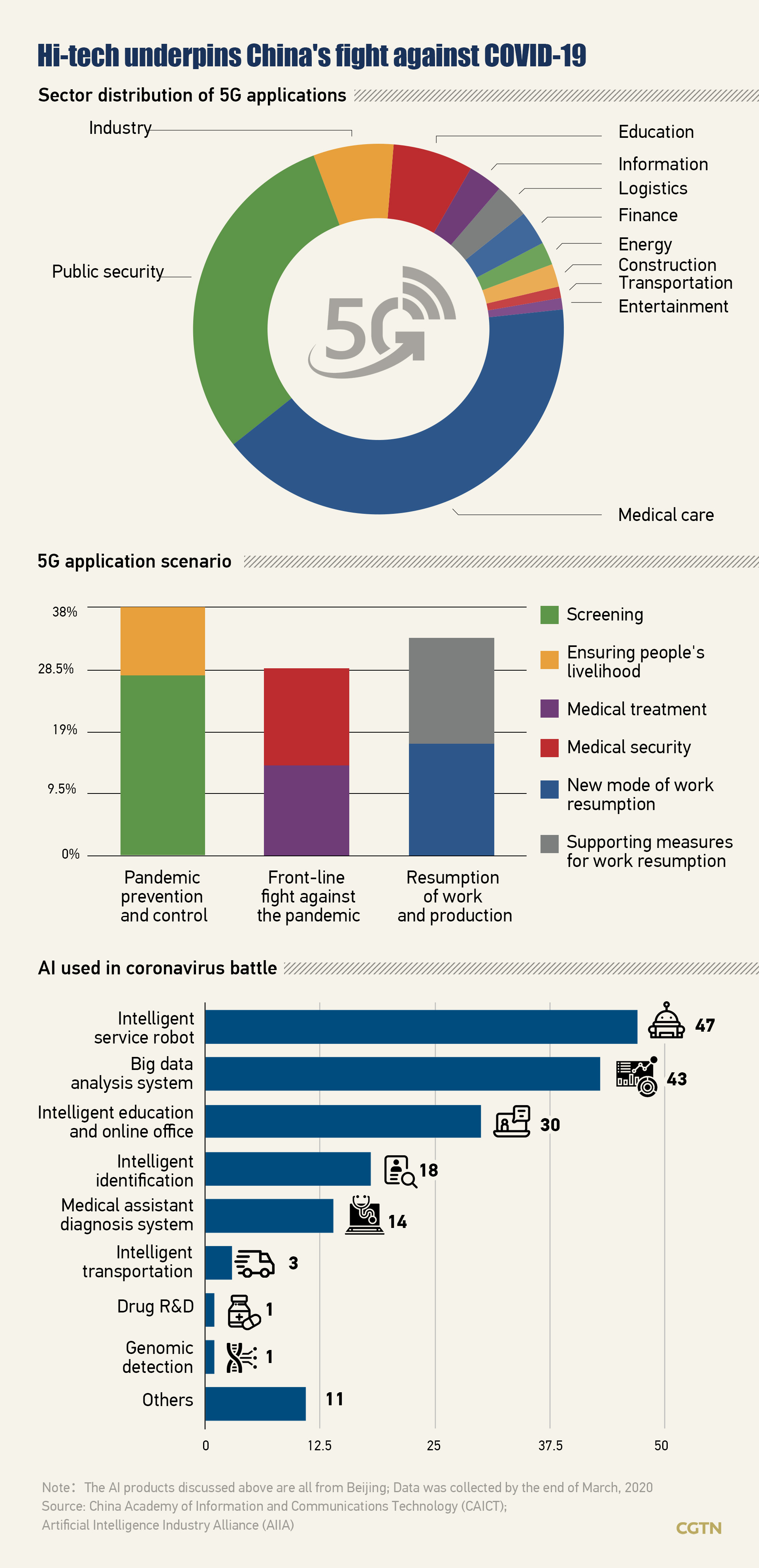
From 5G robots, clinically applicable AI system, to thermal camera-equipped drones, China has witnessed faster and more extensive use of technology in various fields since the beginning of the epidemic.
According to a report from China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, 5G applications were used heavily in medical care, public security, education, manufacturing, and logistics sectors amid the pandemic.
The report published in March showed that 22 Chinese provinces and cities implemented 5G applications to battle COVID-19 back then. Among them, the provinces of Zhejiang, Hubei, the former epicenter of the COVID-19 outbreak, Sichuan, Guangdong, as well as Beijing, were the main hubs for 5G application trials.
Big data, artificial intelligence (AI) also made a difference as China shored up weak links in technology-assisted efforts to contain the virus.
Among over 500 anti-epidemic AI products nationwide, Beijing has the largest number of and most abundant ones ranging from intelligent identification to drug R&D thanks to its leading role in AI innovation across China, a report from Artificial Intelligence Industry Alliance (AIIA) showed.
Emerging technology has proven value in China's fight against the pandemic. The pandemic, meanwhile, provides an opportunity for China to accelerate its development of leading and new frontier industries.
The pandemic transformed people's lives and impacted every industry. But it has not slowed innovation – it's amplifying it. No one knows to what extent high technology could reshape the post-COVID-19 world. But as we all know for sure, international coordination, common unity and wisdom of all countries are our best weapon to combat the virus.
(Data edited by Liu Yuyao, graphics by Li Jingjie)

