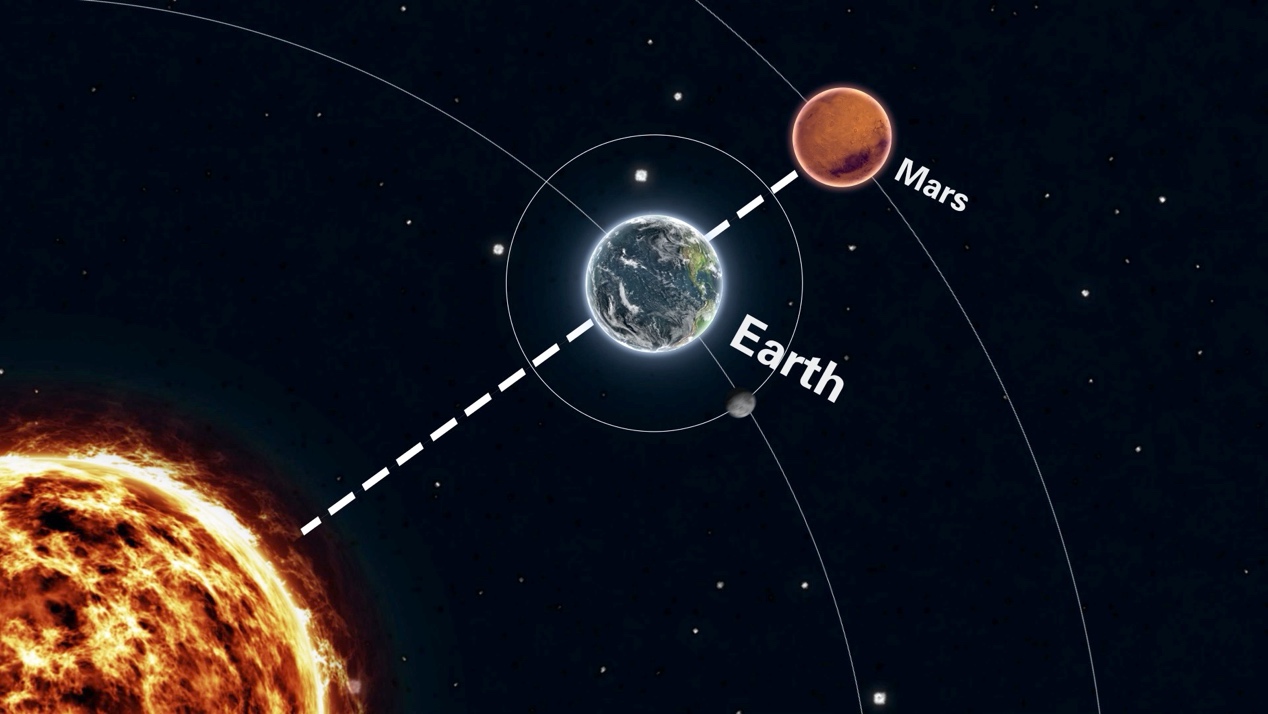
An illustration of the Mars opposition. /CGTN
An illustration of the Mars opposition. /CGTN
Clear your schedule and prepare for a celestial party on Thursday night, as three events will converge in one night: Mars at opposition, the full moon and a lunar occultation.
This week is best for observing the Red Planet, as it will be close to Earth on the opposite side of the Earth to the sun. Mars will remain above the horizon for most of the night, making it an excellent time to see the Red Planet.
For people in the northern hemisphere, look out for the bright-orange object in the northeast sky about 45 minutes after the sun sets in the west.
Xiu Lipeng, a member of the Chinese Astronomical Society and director of the Tianjin Astronomical Society, suggests that stargazers use a telescope to observe more details about Mars opposition.
"With the telescope, you can not only see the color change of the Mars surface but see its white polar cap," he said.
"Don't miss out on this rare opportunity. The next Mars in opposition, when there's also a full moon, will be on February 27, 2059," said Xiu.
What is Mars opposition?
Mars opposition is when the sun, the Earth and Mars are aligned, with the Earth sitting in the middle. This phenomenon happens every 26 months, giving the shortest distance between Mars and Earth.
The last Mars opposition was on October 14, 2020, a year that was called the year of Mars. Three missions were launched toward the Red Planet that year – NASA's Perseverance, the United Arab Emirates' first-ever interplanetary Hope Mars mission and China's first Mars exploration mission-Tianwen 1.
However, the day of Mars opposition is not the ideal launch window for a Mars probe. In fact, it is about two months before the opposition. Because the Earth moves much faster than Mars, scientists say the optimal launch window was from mid-July to mid-August this year, following the most fuel-efficient orbit. During that time, the Earth and Mars will be at a relatively short distance from each other, but not the closest distance.
Based on space technology, the probe will follow an elliptical Earth-Mars transfer orbit called a Hohmann transfer orbit. After flying for around seven months, the probe will eventually be captured by the gravity of Mars and move into the Red Planet's orbit.
01:56

If the scientists had missed the launch window in 2020, they would have had to wait another 26 months to try again in 2022.
The European Space Agency said in March that it was suspending cooperation with Russia's Roscosmos space agency on their joint ExoMars rover mission to search for signs of life on the surface of Mars, resulting in it missing its shot to Mars this year.
China launched its first Mars mission, Tianwen-1, on July 23, 2020, sending an orbiter, a lander and a rover to the Red Planet.
Learn more about the Tianwen-1 launch here.