00:42
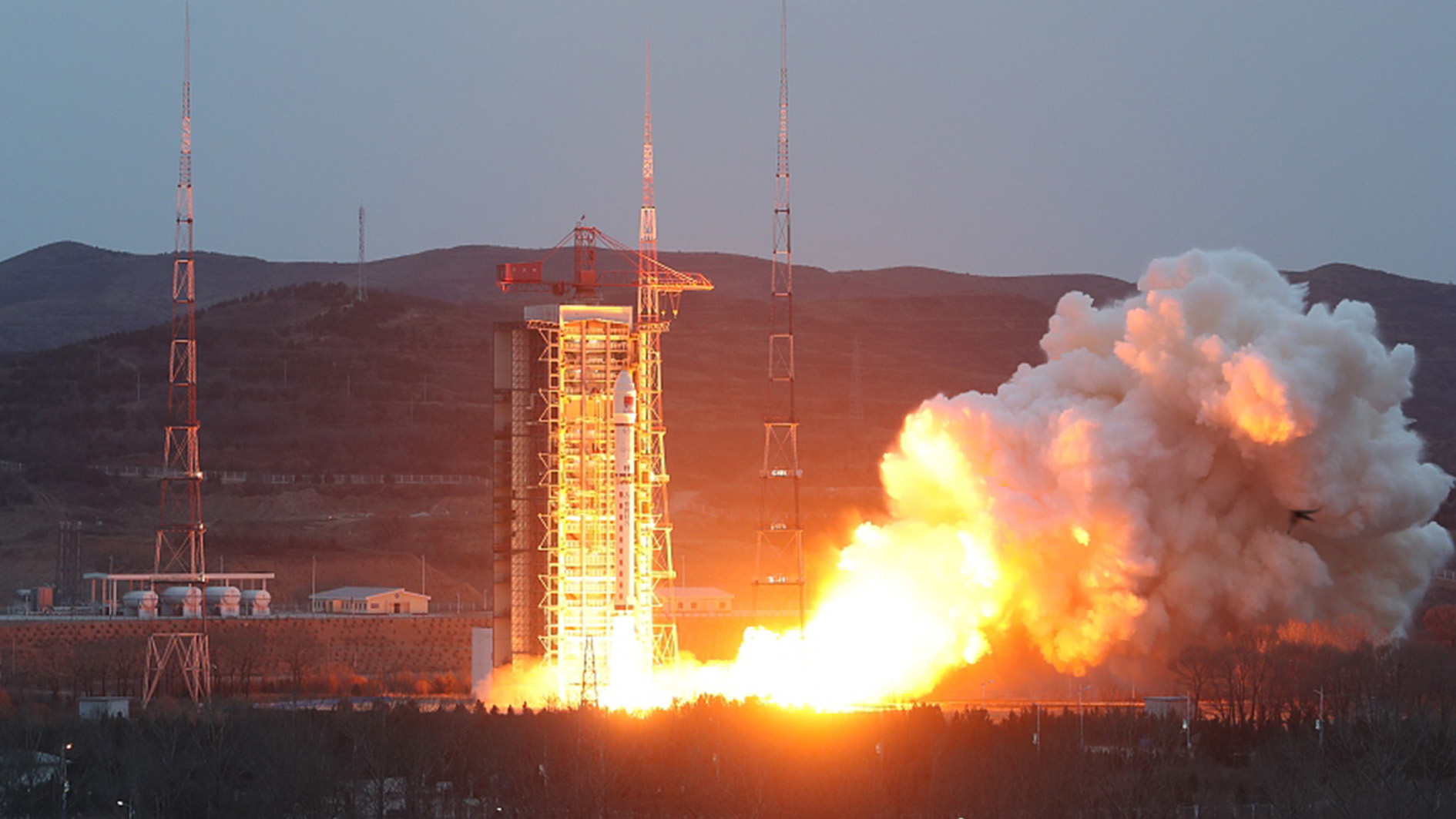

China launched four interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) satellites of its PIESAT-1 constellation via a Long March-2D rocket to provide commercial remote sensing data services at the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center on Thursday.
The four satellites of this mission, composed of a master satellite and three assistant satellites, are the world's first X-band InSAR Earth imaging system in four-satellite formation. The master satellite weighs about 320 kilograms, while a single assistant satellite weighs about 270 kilograms, according to GalaxySpace, the developer of the satellites.
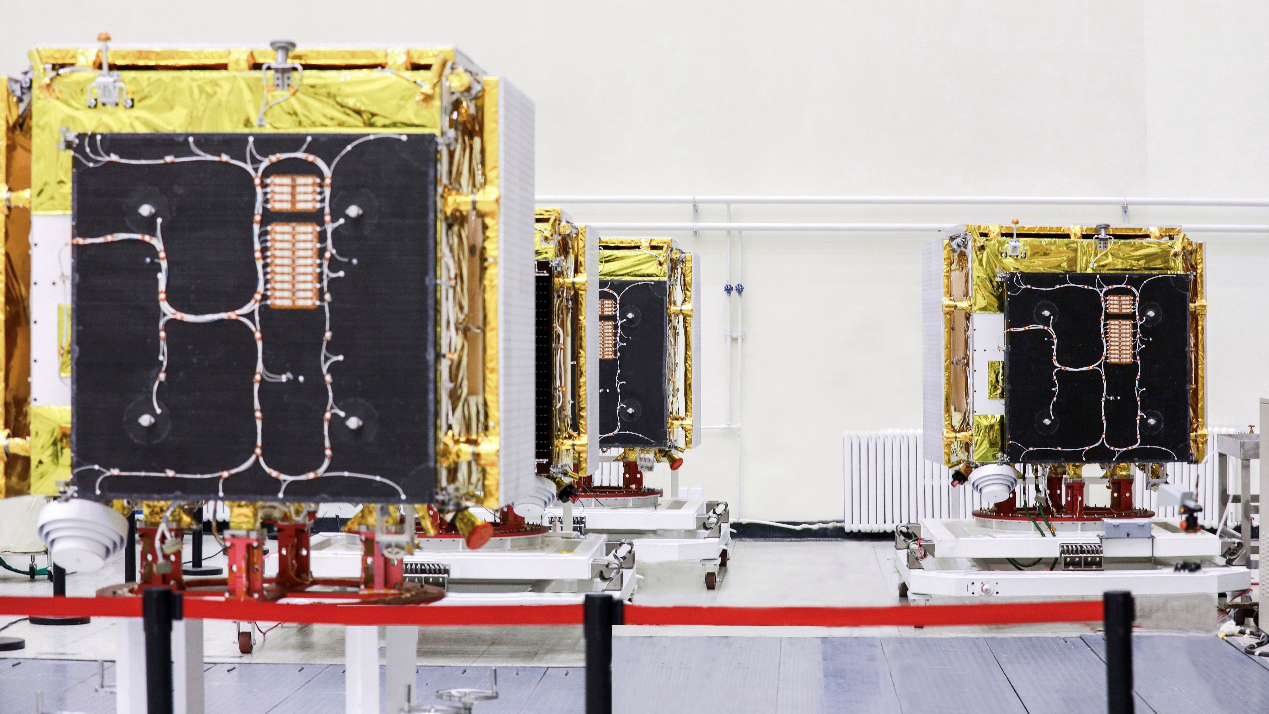
GalaxySpace's four interferometric synthetic aperture radar satellites. /GalaxySpace
GalaxySpace's four interferometric synthetic aperture radar satellites. /GalaxySpace
These satellites in orbit also constitute the first wheel-pattern satellite formation in the world, with the master satellite located in the middle and the three assistant satellites evenly distributed on the wheel hub. The formation uses inter-satellite communication links and phase synchronization links to enable precise orbit control, so as to ensure its stability and spatial safety.
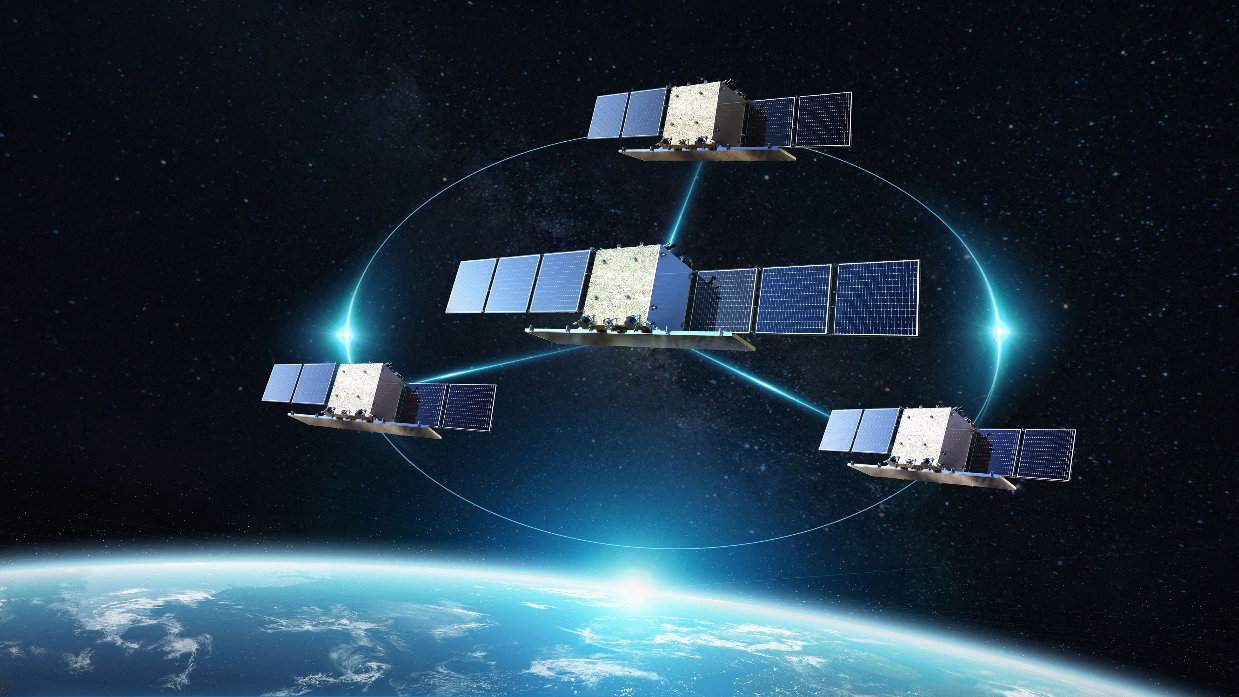

A simulation diagram of the PIESAT-1 constellation, the world's first four-satellite X-band interferometric synthetic aperture radar system. /GalaxySpace
A simulation diagram of the PIESAT-1 constellation, the world's first four-satellite X-band interferometric synthetic aperture radar system. /GalaxySpace
GalaxySpace said the wheel-pattern formation has the advantages of relatively stable formation configuration, multiple interference baselines and high mapping efficiency, compared with traditional interferometric satellite systems.
These satellites are competent in mapping global non-polar regions at a scale of 1:50000, which can achieve the high-precision mapping of global continents in a rapid and efficient manner, the company said.
These satellites are a "powerful tool" for early identification of major geological hazards in complex areas thanks to their millimeter-level deformation monitoring capability that can provide data support for the exploration and prevention of land subsidence, collapse, landslides and other disasters, GalaxySpace added.
With the sub-meter imaging capability in high resolution and wide range, these satellites can provide high-quality imaging and observation of the ground round the clock.