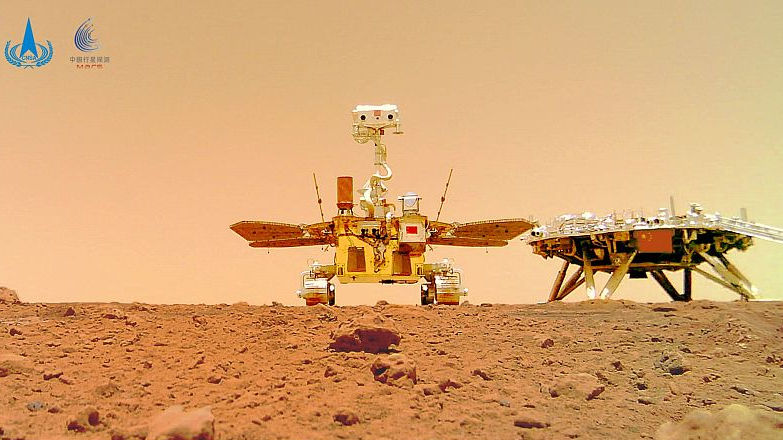

The image taken by a camera released from China's Zhurong Mars rover shows the rover (L) and the landing platform on the surface of Mars, June 11, 2021. /China National Space Administration via CFP
The image taken by a camera released from China's Zhurong Mars rover shows the rover (L) and the landing platform on the surface of Mars, June 11, 2021. /China National Space Administration via CFP
China's first Mars rover, Zhurong, has still been in dormant mode since it encountered a dust storm on the surface of the planet in May last year, a Chinese scientist confirmed in an exclusive interview with China Media Group (CMG) on Tuesday.
The rover will automatically power on when the two conditions are met at the same time: the temperature in the cabin is higher than minus 15 degrees Celsius and the solar power generation meets the minimum daily power consumption (140 watts) of the rover, Zhang Rongqiao, chief designer for China's Mars exploration program, told CMG.
Despite the patrol area of Zhurong having entered the spring season, the rover is yet to be revived.
"Based on our analysis, the most likely possibility is that an unpredictable accumulation of Martian dust has led to a decrease in the power generation capacity, which is insufficient to wake it up," Zhang explained.
Zhurong, named after the god of fire in Chinese mythology, is a solar-powered rover. It landed on Mars in May 2021.
'Within expectation'
Given the harsh weather conditions on Mars, the design team had taken dust into consideration when designing the rover.
If the buildup of dust was 30 percent higher than the amount engineers had planned for, the rover would need to wait for the strongest sun rays to restore power generation capacity. If the dust accumulation has exceeded 40 percent of the planned amount, it might not wake up anymore, Zhang said.
He added the Mars rover being inactive now is within the team's expectations as part of the experimental project.
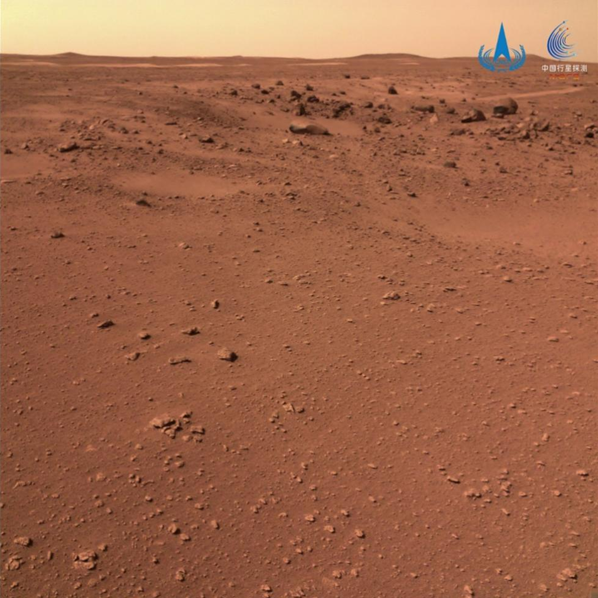
An image shows rocks distributed near impact craters on the surface of Mars, taken by the navigation terrain camera onboard Zhurong, April 10, 2022. /China National Space Administration via Xinhua
An image shows rocks distributed near impact craters on the surface of Mars, taken by the navigation terrain camera onboard Zhurong, April 10, 2022. /China National Space Administration via Xinhua
Zhurong, with a designed lifetime of 90 Martian days, patrolled on the planet for 358 Martian days and made various contributions to Mars exploration before it switched to dormant mode. Scientists said the mission has significantly exceeded expectations.
Read more:
China's Mars exploration goes far beyond: Chief Designer
China releases its first color-coded global map of Mars