
A Fuxing bullet train runs on the Lhasa-Nyingchi railway in southwest China's Xizang Autonomous Region, April 14, 2022. /Xinhua
A Fuxing bullet train runs on the Lhasa-Nyingchi railway in southwest China's Xizang Autonomous Region, April 14, 2022. /Xinhua
Oizhu Doje, a resident of Baka Village in Ngari Prefecture in southwest China's Xizang Autonomous Region, has witnessed how infrastructural development brings prosperity to the village.
Recalling the times when villagers could not transport willow trees due to road blockages amid heavy snow, Oizhu Doje now appreciates the asphalt road that became operational at the end of 2020.
"The willow trees brought an income of 910,000 yuan (around $130,000) for villagers the year after the asphalt road was put into use," said Oizhu Doje
What Baka village has experienced epitomizes how Xizang has sought to accelerate the infrastructural building to improve its residents' well-being.
Official statistics show that the total length of roads in Xizang has increased by some 55,000 kilometers to 120,000 kilometers from 2012 to 2022.
Along with the fast development of infrastructure, Xizang also saw rapid economic growth in the past decade. In the first quarter of this year, Xizang's GDP reached 57.587 billion yuan, an increase of 8.2 percent year on year – one of the highest in China.
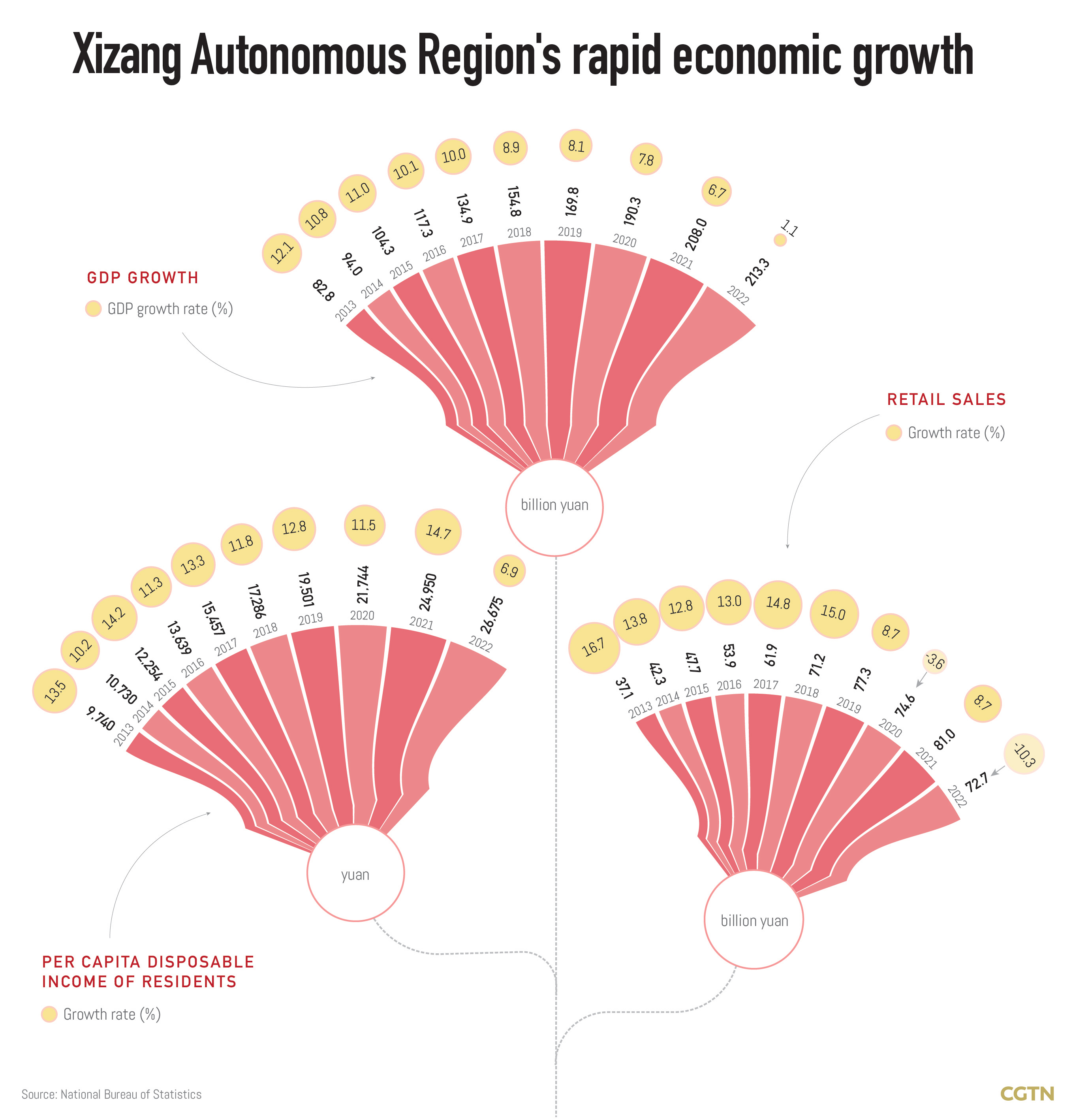
From 2012 to 2021, Xizang's GDP grew by an annual average of 9.5 percent and the growth rate has been among the top in the country for years, said Tian Guanghua, deputy director of regional development and reform commission at a press conference in October 2022.
The per capita GDP in Xizang exceeded 56,800 yuan in 2021, realizing an average annual growth of 7.6 percent over the decade, Tian added.
The remarkable growth has much to do with the government support. Tian said at the press conference that from 2012 to 2021, 525 projects were implemented with a total investment of 682.6 billion yuan, of which 530.9 billion yuan was invested by the central government.
Chinese President Xi Jinping stressed writing a new chapter of lasting stability and high-quality development for the plateau region during his visit to Xizang in July 2021.
During the visit, Xi also noted the development of distinctive industries, the building of national bases for clean energy and coordination between development and security.
Responding to the central authorities' guidelines on high-quality development, Xizang has made progress in various areas including clean energy, green development and high-end digital technology.
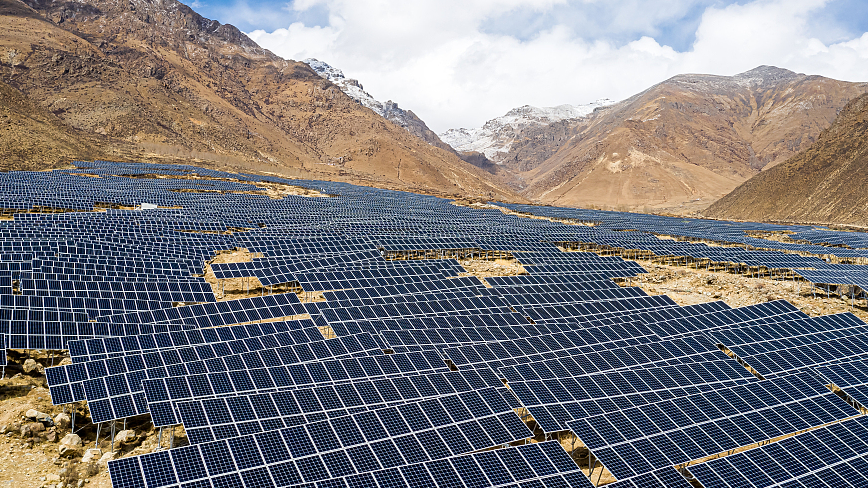

A solar power plant in Lhasa City, southwest China's Xizang Autonomous Region, April 4, 2021. /CFP
A solar power plant in Lhasa City, southwest China's Xizang Autonomous Region, April 4, 2021. /CFP
Located on the southwestern part of the resource-rich Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, Xizang leads the country with 174 gigawatts of potential hydropower, according to the white paper "Ecological Progress on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau" issued in July 2018.
In November 2022, a 1,200-megawatt hydropower project started operation on the border of Xizang and southwest China's Sichuan Province – the first hydropower station in the upper reaches of the Jinsha River.
As outlined in Xizang's latest five-year plan (2021 to 2025), it aims to boost the development of solar power generation, pushing the total installed capacity to above 10 gigawatts by 2025.
"Developing clean energy shows the idea of 'lucid waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets' and the harmonious coexistence of humanity and nature in Xizang," said Chen Pu, deputy director of the institute of the economic strategy at the Xizang Academy of Social Sciences.
Home to highland barley -the main crop in the special geographical and ecological conditions of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the Xizang regional government has introduced measures including building a number of highland barley cultivation bases to improve varieties and has forstered green organic barley brands to enhance the brand of highland barley, thus helping increase residents' income and further promote rural revitalization.
High-end digital technology also plays a major role in Xizang's pursuit of high-quality development.
Shigatse is a major agrarian city where the highland barley output accounts for nearly half of the total output of the region. To promote the quality and efficiency of the highland barley industry, the city established a highland barley industry big data platform in 2023 to deal with businesses including highland barley planting, seed traceability and agricultural machinery management.
By developing smart agriculture and animal husbandry, Xizang has cultivated a number of backbone enterprises and strived to keep an annual grain output above 1 million tonnes, with total output value of agricultural and livestock product processing reaching 7.5 billion yuan.
Xizang is also actively exploring and cultivating new forms of business in the digital economy. This year, Xizang plans to launch 30 industrial digital transformation projects, build a number of digital workshops and smart factories, and set up cloud-based platforms for more than 300 enterprises.
Despite the fast growth, Yin Yongwei, an official from the regional development and reform commission, cautioned that the imbalanced regional development and imbalanced internal and external opening-up are among the factors challenging Xizang's aim of building a pilot zone of high-quality development for the plateau.
Xing Guangcheng, head of the Institute of Chinese Borderland Studies at the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, spoke highly of Xizang's geographic strategy, saying that the region could enhance economic cooperation with South Asian countries with the help of the Belt and Road Initiative.