
Tech & Sci
20:13, 26-Dec-2017
126,000 Beijing households cease using coal stoves in 2017
Local Beijing authorities said on Tuesday that up to 126,000 more households in the Chinese capital began to use clean-energy-fueled heating facilities instead of highly polluting coal stoves this year.
With an investment of 7.4 billion yuan (1.1 billion US dollars), the city completed 296 clean energy projects in rural areas this year, reducing the city's annual coal use by 2.08 million tons.
As part of a campaign launched in 2013 to replace coal with cleaner fuel, Beijing has phased out coal-fired heating facilities in 185,000 households across 415 villages, reducing the city's coal use by 18 million tons over five years.
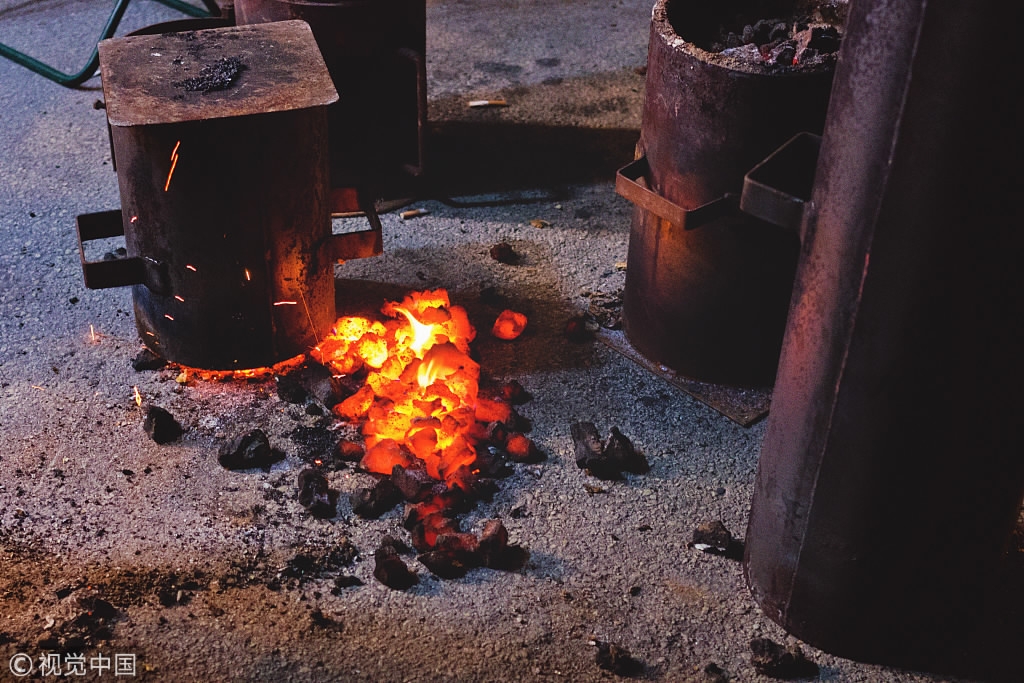

By shifting to clean fuel, such as electricity and gas, Beijing can cut the emission of carbon dioxide by nearly 600,000 tons. /VCG Photo
By shifting to clean fuel, such as electricity and gas, Beijing can cut the emission of carbon dioxide by nearly 600,000 tons. /VCG Photo
Beijing will phase out coal-fired heating facilities in 217,000 households between 2016 and 2020. By shifting to clean fuels, such as electricity and gas, the city can cut carbon dioxide emissions by nearly 600,000 tons, particulate matter by 3,700 tons and sulfur dioxide by nearly 1,500 tons.
Small stoves in Beijing's suburban and rural areas, not covered by the central heating system, have been blamed for largely contributing to the city's smog during the winter.
According to Beijing Gas, the consumption volume of natural gas in Beijing has maintained an annual growth rate of 15 percent in recent years.
2km
Source(s): Xinhua News Agency

SITEMAP
Copyright © 2018 CGTN. Beijing ICP prepared NO.16065310-3
Copyright © 2018 CGTN. Beijing ICP prepared NO.16065310-3