
Tech & Sci
23:06, 03-Aug-2017
China's 'Great Bay Area', a place of abundant resources

China's Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area is rich in resources and has great potential for development and utilization, said China Geological Survey (CGS) of the Ministry of Land and Resources in a recently released book illustrating the area's natural resources and the environment.
Eight-billion-ton oil resources have been estimated in the area. Eleven prospecting areas and 19 metallogenic areas have been outlined. Two mines of 100 billion cubic meter level have also been located.

The Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge. /Xinhua Photo
The Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge. /Xinhua Photo
The area also enjoys tremendous potential in the emergency water supply as it has about 15-billion-cubic-meter underground fresh water reserves annually.
The regional crust of the Great Bay Area is also relatively stable, which provides a sound engineering geological condition. With relatively smooth terrain, the offshore area is suitable for port construction.
Ample reserved land resources – 7,225-square-kilometer mud flats and neritic areas – offer properties for engineering and urban construction.
The CGS has suggested that local governments strengthen the efforts in exploration and development of oil gas and NGH, actively promote the industrialization of NGH exploitation, and push forward the protection as well as the exploitation of geological relics, optimizing the layout of modern industry in this area.
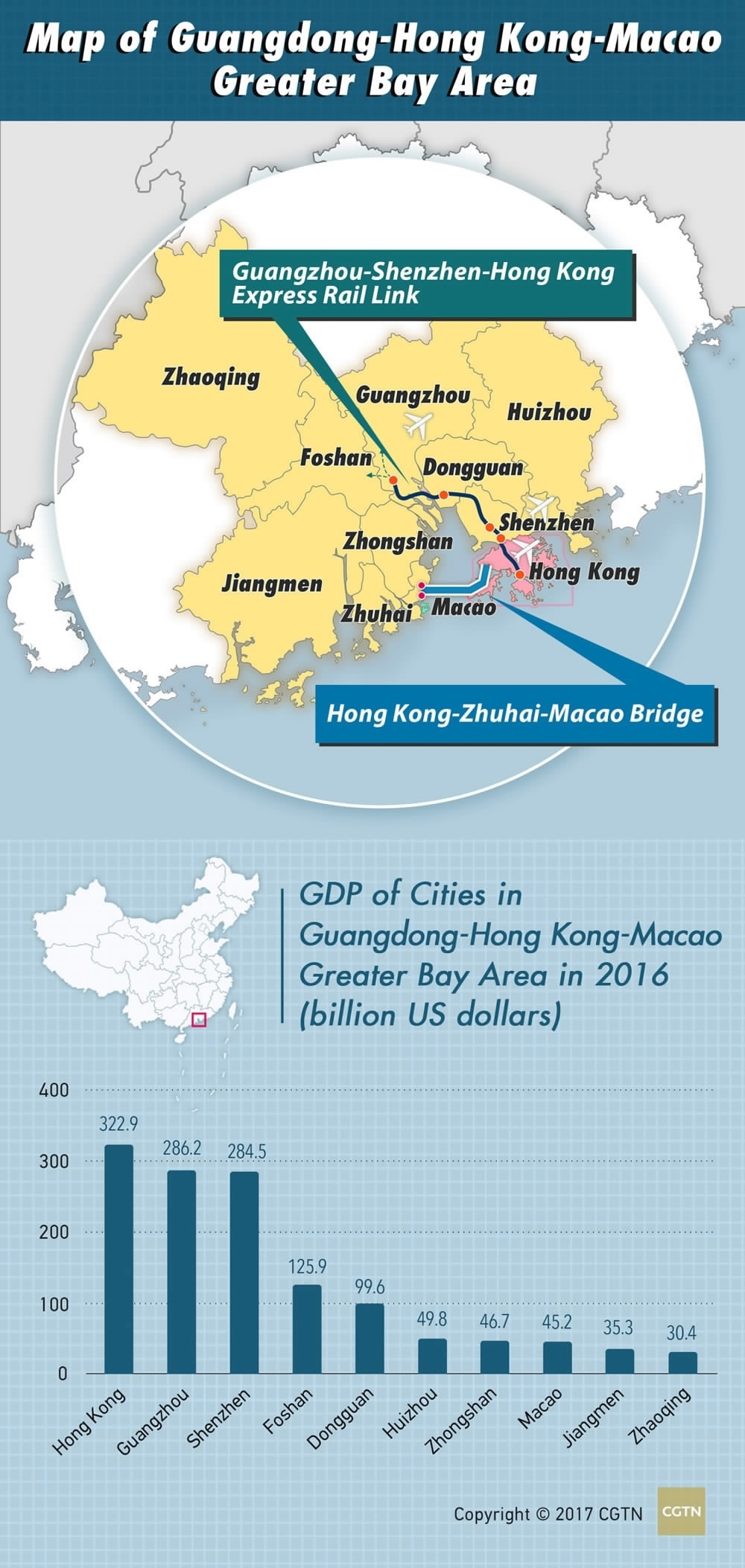
CGTN graphic
CGTN graphic
Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area incorporates nine cities in southern China's Guangdong Province and two Special Administrative Regions, Hong Kong and Macao, covering 56,000-square-kilometer land areas and a total of 3,201-kilometer continental and island coastlines.
The idea of establishing a Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area was initiated in China's 13th Five-Year Plan (2016-2020), and mentioned in the government's work report this year.

SITEMAP
Copyright © 2018 CGTN. Beijing ICP prepared NO.16065310-3
Copyright © 2018 CGTN. Beijing ICP prepared NO.16065310-3