03:28
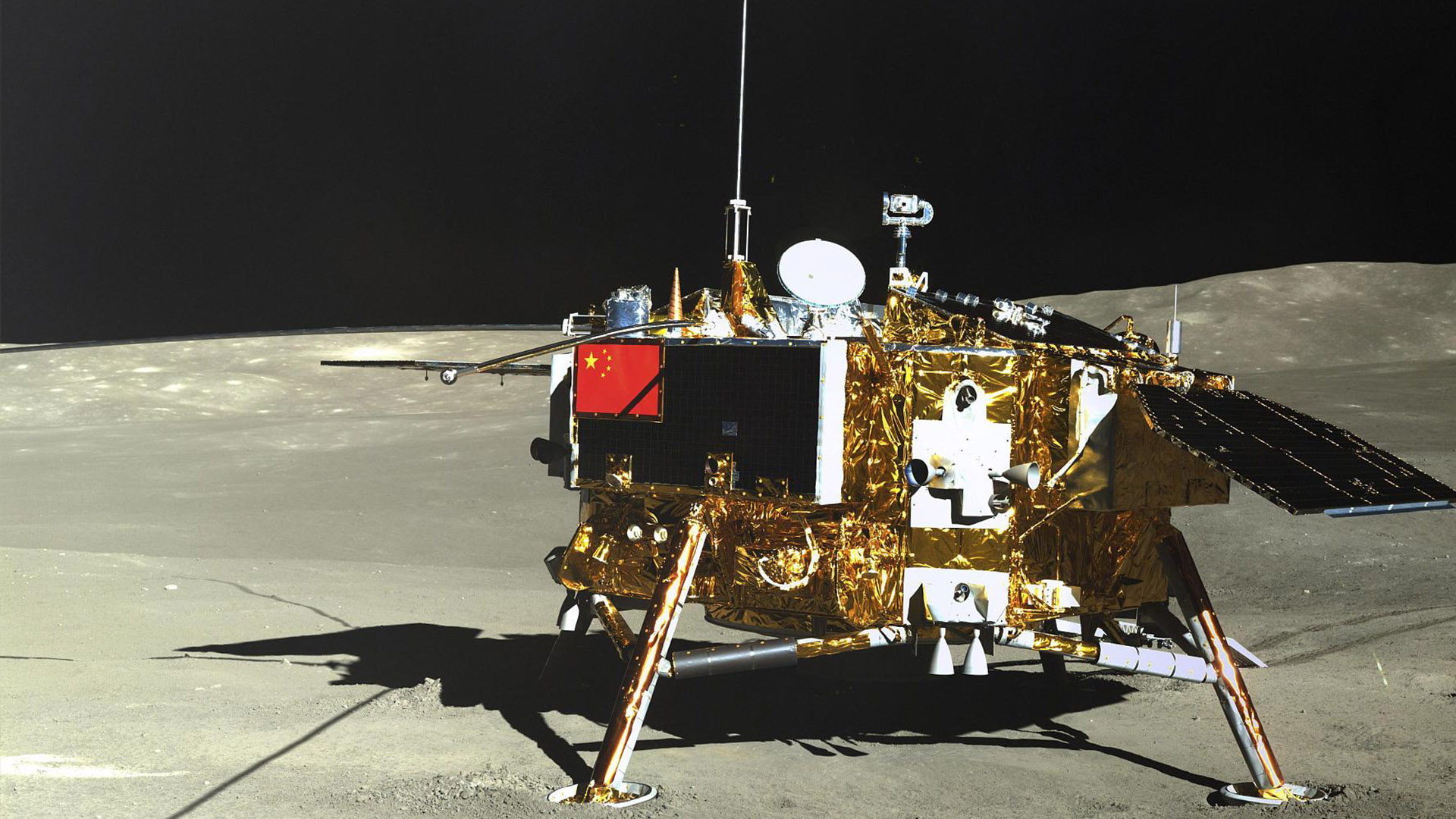
As we approach the 50th anniversary of man landing on the moon, a different group of living creatures will now make headway there. A team of scientists from Chongqing University is sending a small biological payload aboard the Chang'e-4 spacecraft. So what does the biological payload consist of?
It's been said that good things come in small packages. This small tin is not even 3 kilograms.
But thanks to its installation on the lander of the Chang'e-4 spacecraft, it has made history.
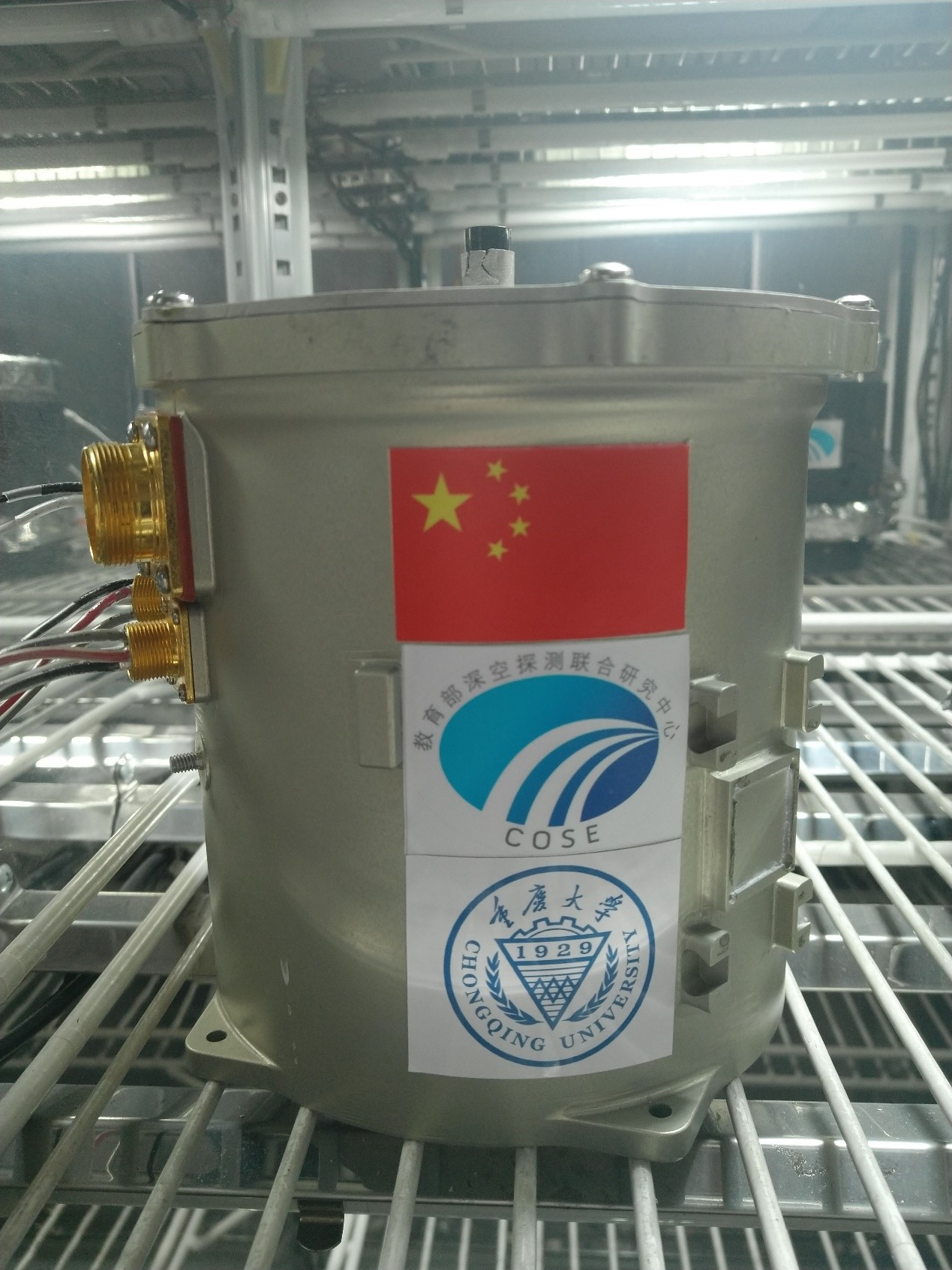

The tin is mankind's first biological payload on the moon. /Chongqing University Photo
The tin is mankind's first biological payload on the moon. /Chongqing University Photo
The six passengers inside? Seeds of cotton, potato, Arabidopsis, rapeseed, fruit fly pupa and yeast.
Professor Xie Gengxin is the Chief Designer of this biological experiment payload on the Chang'e-4. He told CGTN that there are animal, plants and microorganisms in this payload, creating a micro-ecosystem. They used a light pipe to guide the sunlight inside the tin, they will study their photosynthesis under strong sunlight.
The lunar environment features low gravity, bright sunlight and radiation. Professor Xie says the water inside the payload has been released, and the seeds will soon sprout.
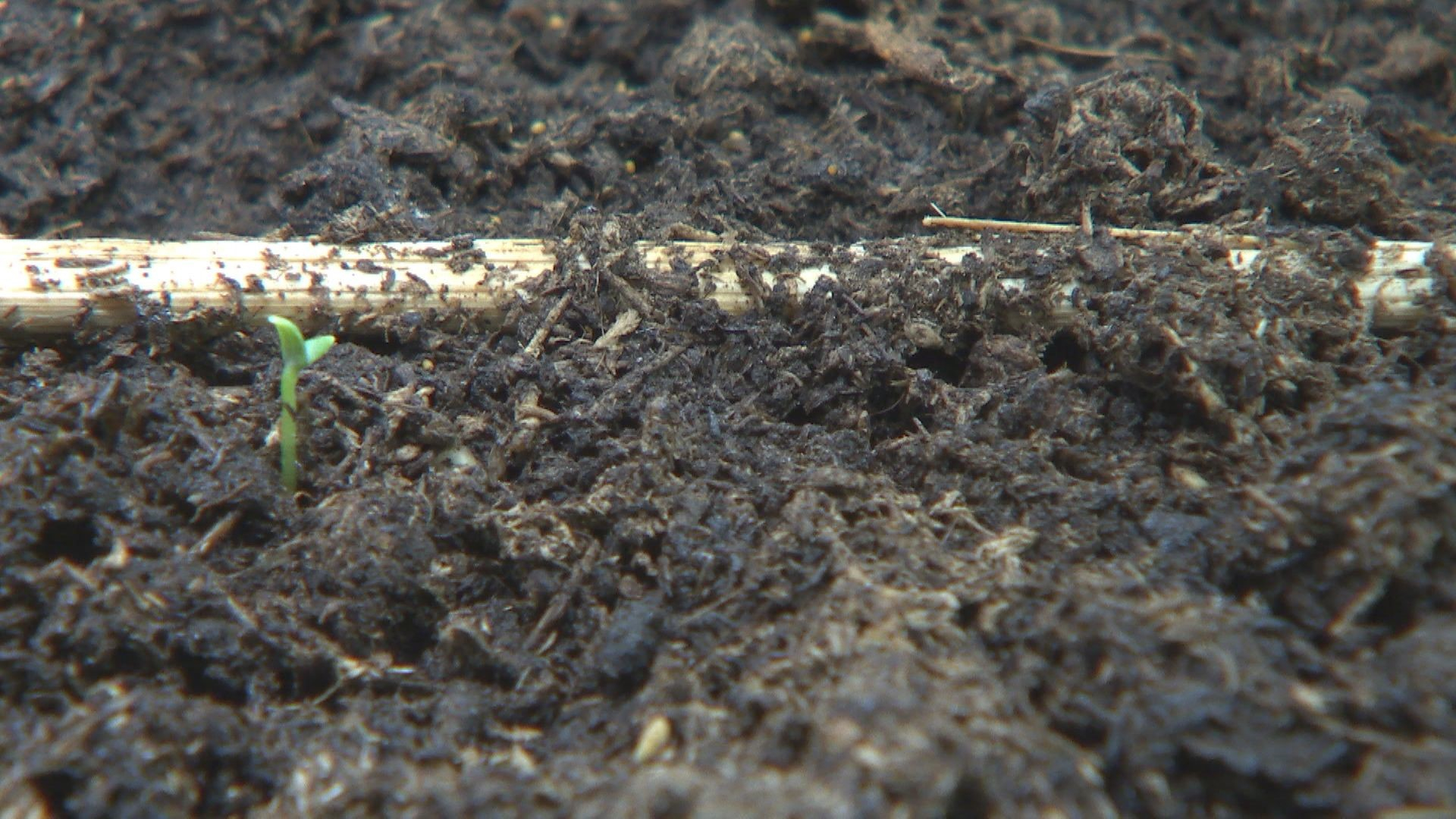

But how many will spring up on the moon still needs to be confirmed, with the latest images expected very soon. /CGTN Photo
But how many will spring up on the moon still needs to be confirmed, with the latest images expected very soon. /CGTN Photo
To better understand how plants and animals grow in different environments, scientists have set up two identical payloads which start simultaneously with the one on the moon. As we can see, one of the cotton seeds has already sprouted here on earth.

Scientists have set up two identical payloads which start simultaneously with the one on the moon, one of the cotton seeds already sprouted on earth. /CGTN Photo
Scientists have set up two identical payloads which start simultaneously with the one on the moon, one of the cotton seeds already sprouted on earth. /CGTN Photo
Professor Xie says one of the key challenges is to control and adjust the temperature within such a small area. They have tried many new materials and technologies. Researchers from Chongqing University are now monitoring the growth data 24 hours a day, and recording the latest condition accordingly. Since 2015, researchers and scientists from Chongqing University have brought this project from idea to reality.
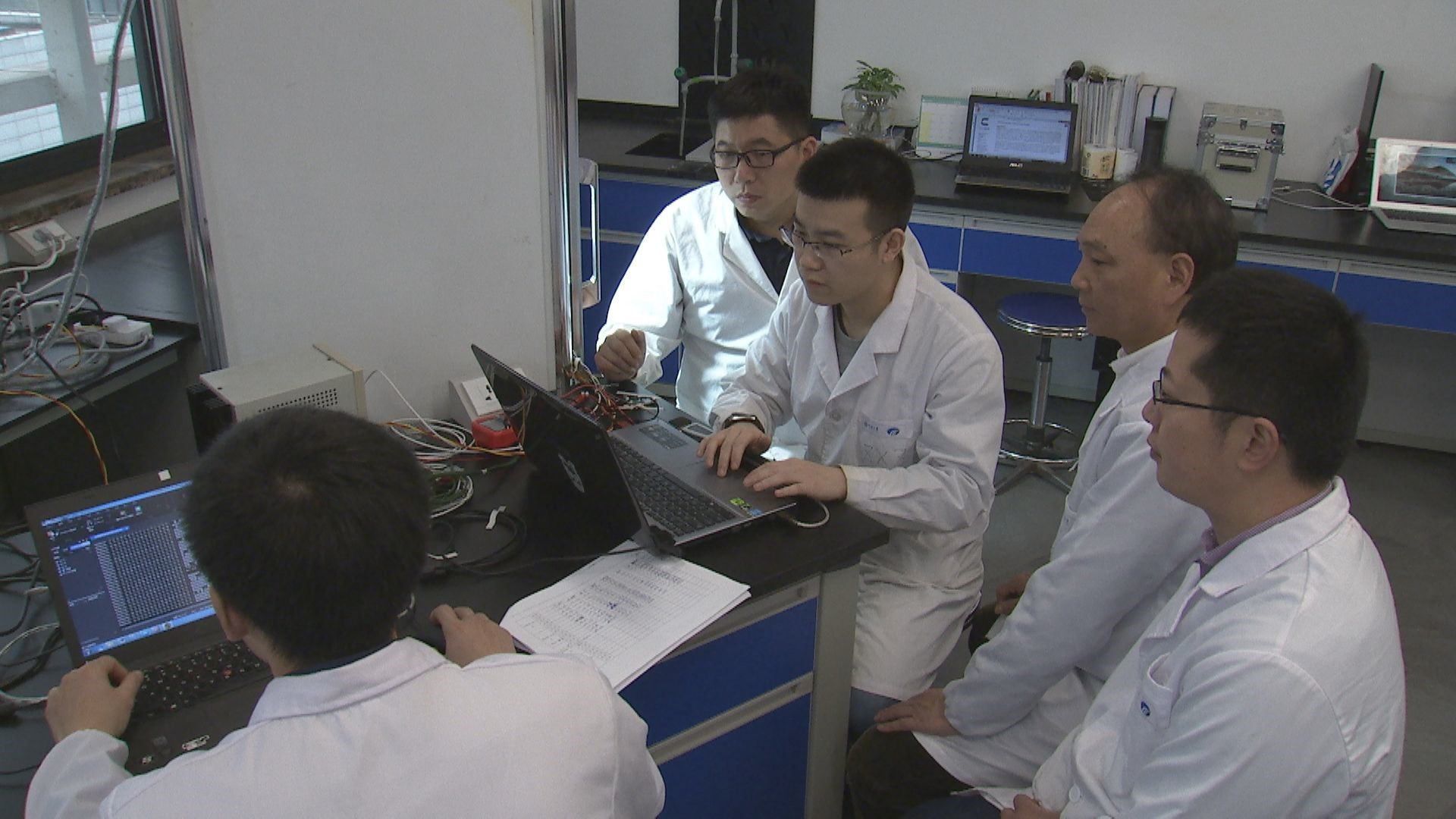

Researchers from Chongqing University are now monitoring the growth data 24 hours a day, and recording the latest condition accordingly. /CGTN Photo
Researchers from Chongqing University are now monitoring the growth data 24 hours a day, and recording the latest condition accordingly. /CGTN Photo
Liu Hanlong, the Vice President of Chongqing University told CGTN that this biological experiment payload was chosen from almost 300 projects nationwide. Professors and researchers from Chongqing led the way, but they also cooperated with researchers from over 20 domestic institutes and universities.
Many scientists around the world are wondering whether or not these plants and animals will pollute the lunar environment.

Professor Xie confirmed that's impossible because the payload is sealed and they have taken every measure to prevent such a thing from happening. /CGTN Photo
Professor Xie confirmed that's impossible because the payload is sealed and they have taken every measure to prevent such a thing from happening. /CGTN Photo
Professor Xie told CGTN that as is known, no air nor oxygen exists on the moon, and the temperature is always very extreme. Even if some of them leaked, they would have no chance of surviving, they would be decomposed to harmless organics with no pollution on the moon.
Regardless of the results, Professor Xie says the team has opened a new chapter in space experiments. After the project is finished, they will study the data carefully, summarize the experience and prepare for their next biological experiment.







