
Culture
11:38, 17-Dec-2018
China's 40 Years: Improvements in daily lives
Updated
11:25, 20-Dec-2018
By Ai Yan

Ever since China launched its epoch-making reform and opening-up policy 40 years ago, daily lives of the Chinese people have gone through dramatic changes.
China's economy has witnessed a meteoric rise in the last four decades. In 2017, the country's gross domestic product (GDP) totaled 82.71 trillion yuan (about 12.84 trillion U.S. dollars), contributing to about 15 percent of the world economy.
But how does this figure help improve the lives of the Chinese people?
United Nation's Human Development Index (HDI) holds the answer.
The HDI emphasizes that people and their capabilities should be the ultimate criteria for assessing the development of a country, not the economic growth alone. It is measured mainly on the basis of three dimensions: health, education and the standard of living.
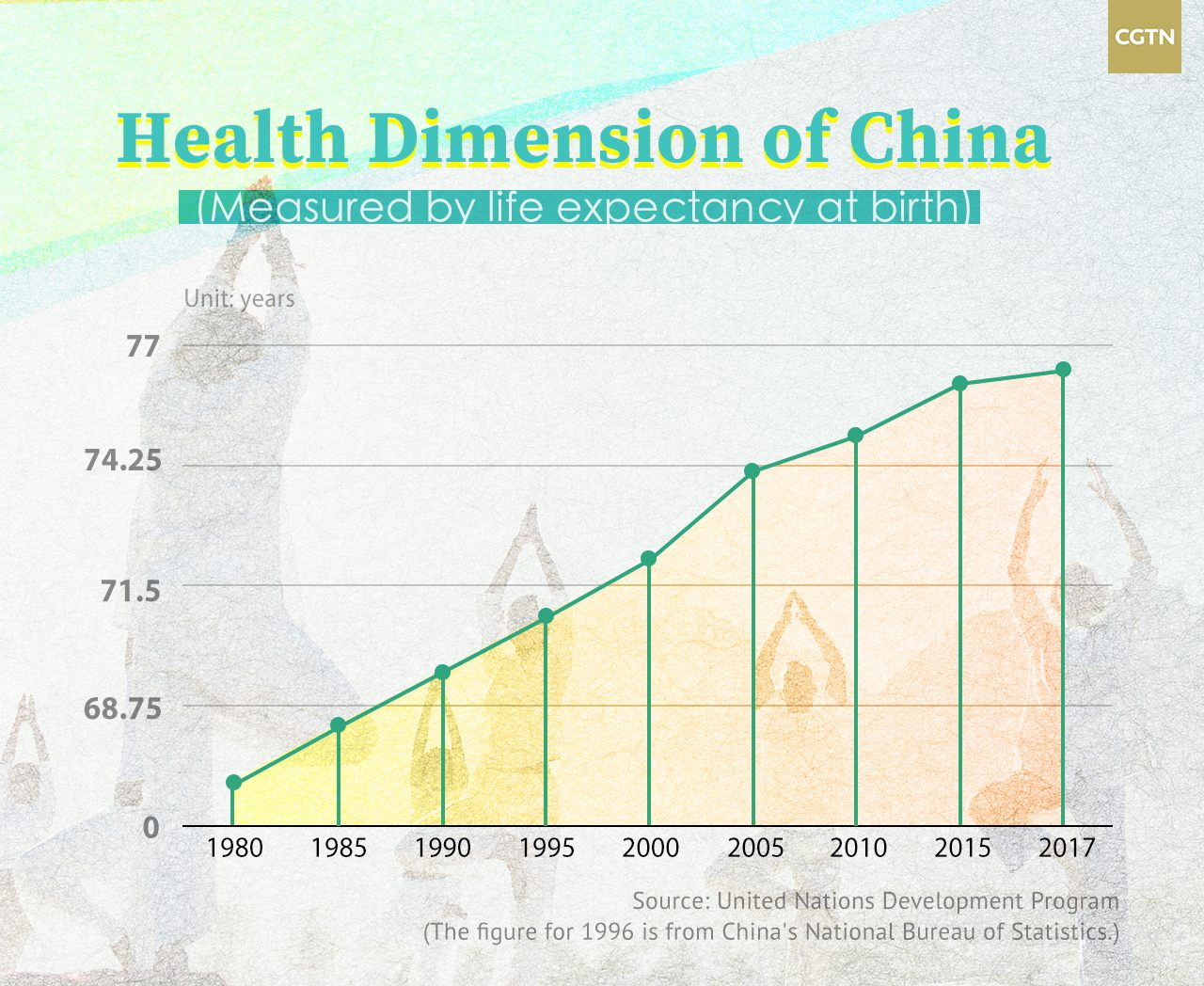
Health Dimension
CGTN Photo
CGTN Photo
Health dimension is assessed by life expectancy at birth. According to the UN data, China's life expectancy at birth has risen from 67 years in 1980 to 76.4 years in 2018.
With the expansion of the Chinese economy, the country's expenditure on healthcare also increased in the past decades.
China's expenditure on healthcare rose from 14.32 billion yuan in 1980 to 5.15 trillion yuan in 2017.
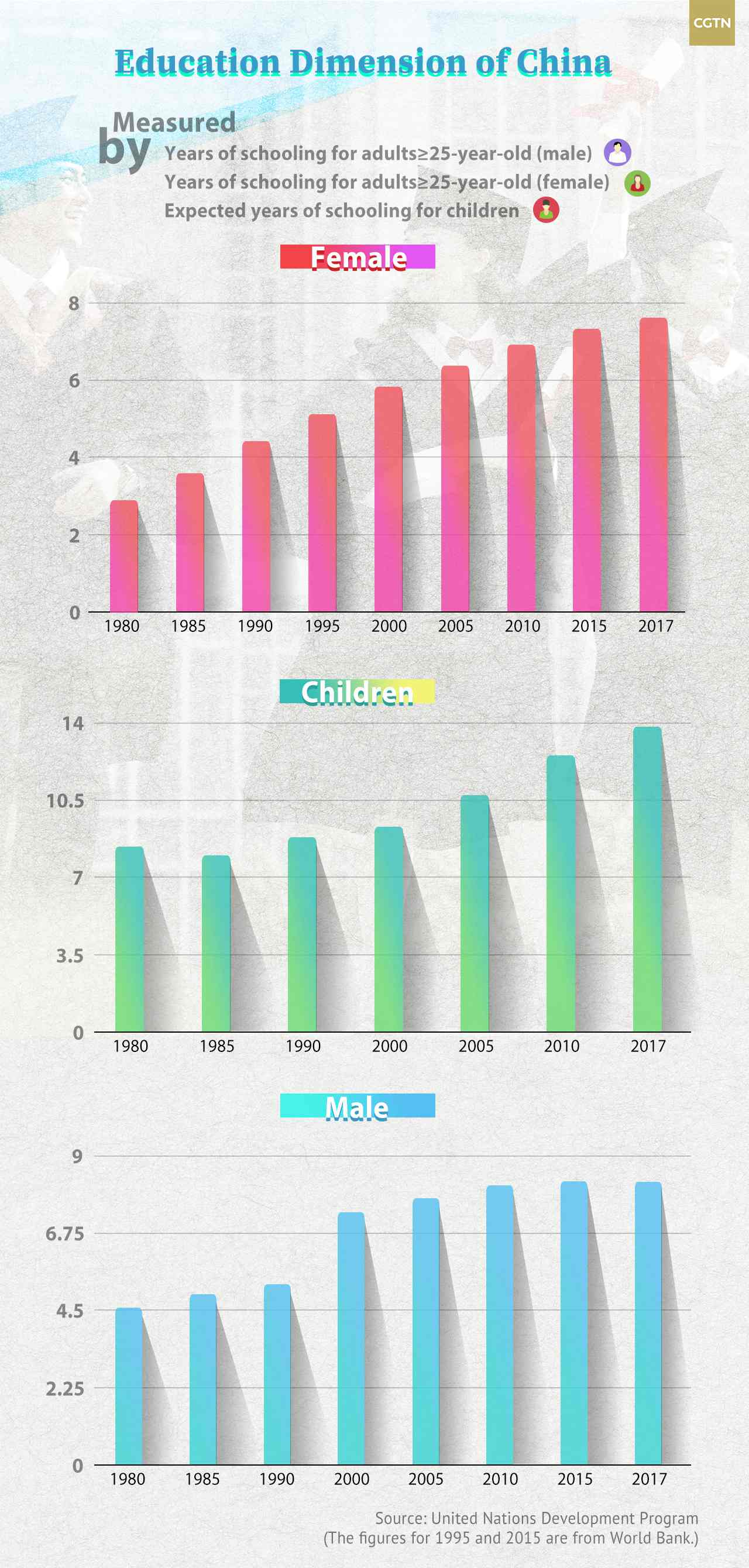
Education Dimension
CGTN Photo
CGTN Photo
Education dimension is measured on the basis of two factors. First, the average number of years of education received in a lifetime by people aged 25 years and older, and second, access to learning and knowledge by expected years of schooling for children of school-entry age.
In 1980, the schooling years for men and women above the age of 25 were 2.9 and 4.6 respectively, while the expected years of schooling for children of school-entry age was 8.4.
In 2017, the figures turned into 8.3, 6.9 and 13.8 respectively.
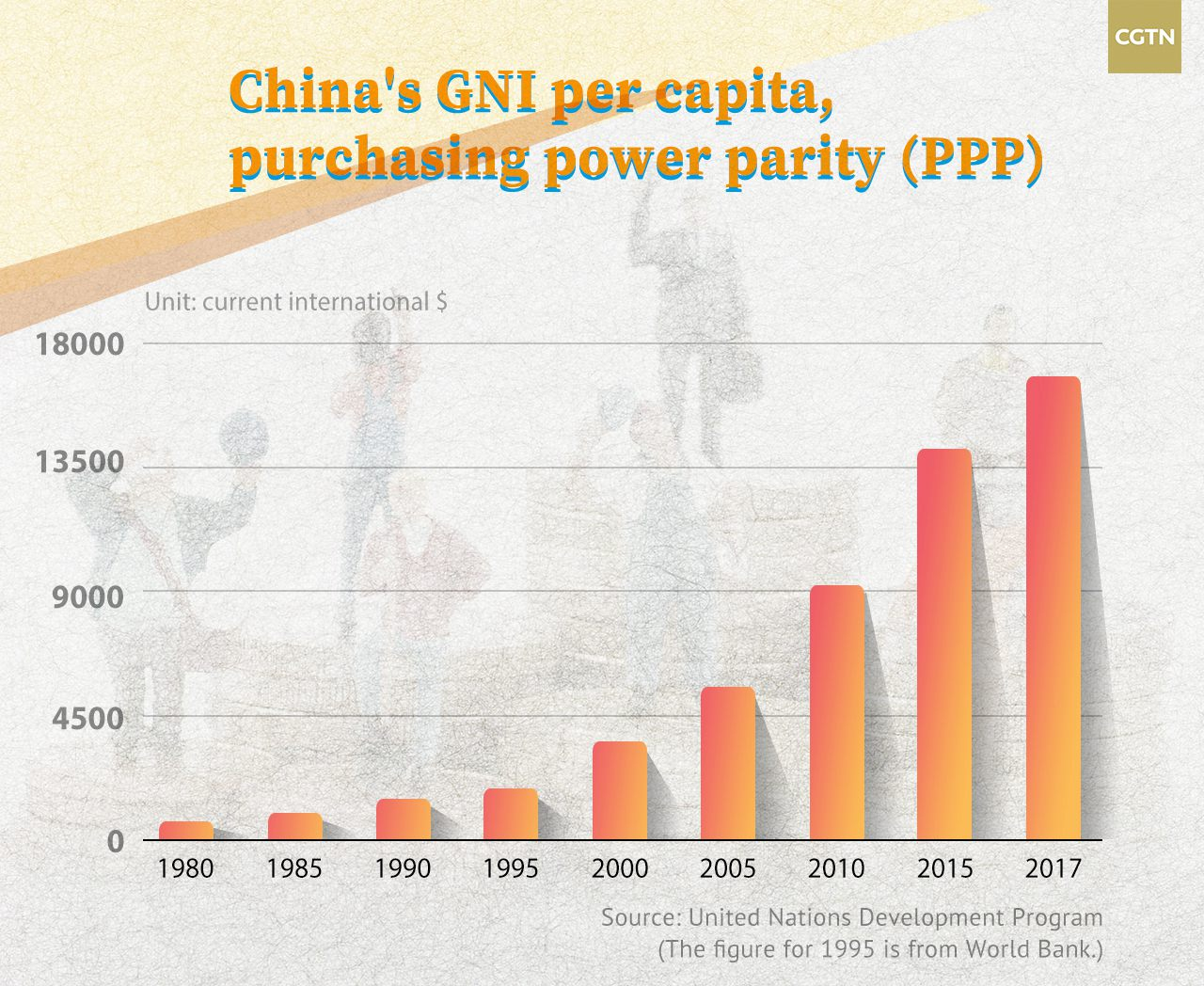
Standard of Living Dimension
The standard of living dimension is measured by gross national income (GNI) per capita in purchasing power parity (PPP) rate. The GNI is the dollar value of a country's final income in a year, divided by its population, which reflects the average income of a country's citizens.
CGTN Photo
CGTN Photo
The World Bank classified countries into four income groupings by measuring the GNI per capital, namely, low, lower-middle, upper-middle and high-income economies. Back in 1980, China's GNI per capita was 690 U.S. dollars, but the number soared to 16,760 U.S. dollars by the end of 2017.
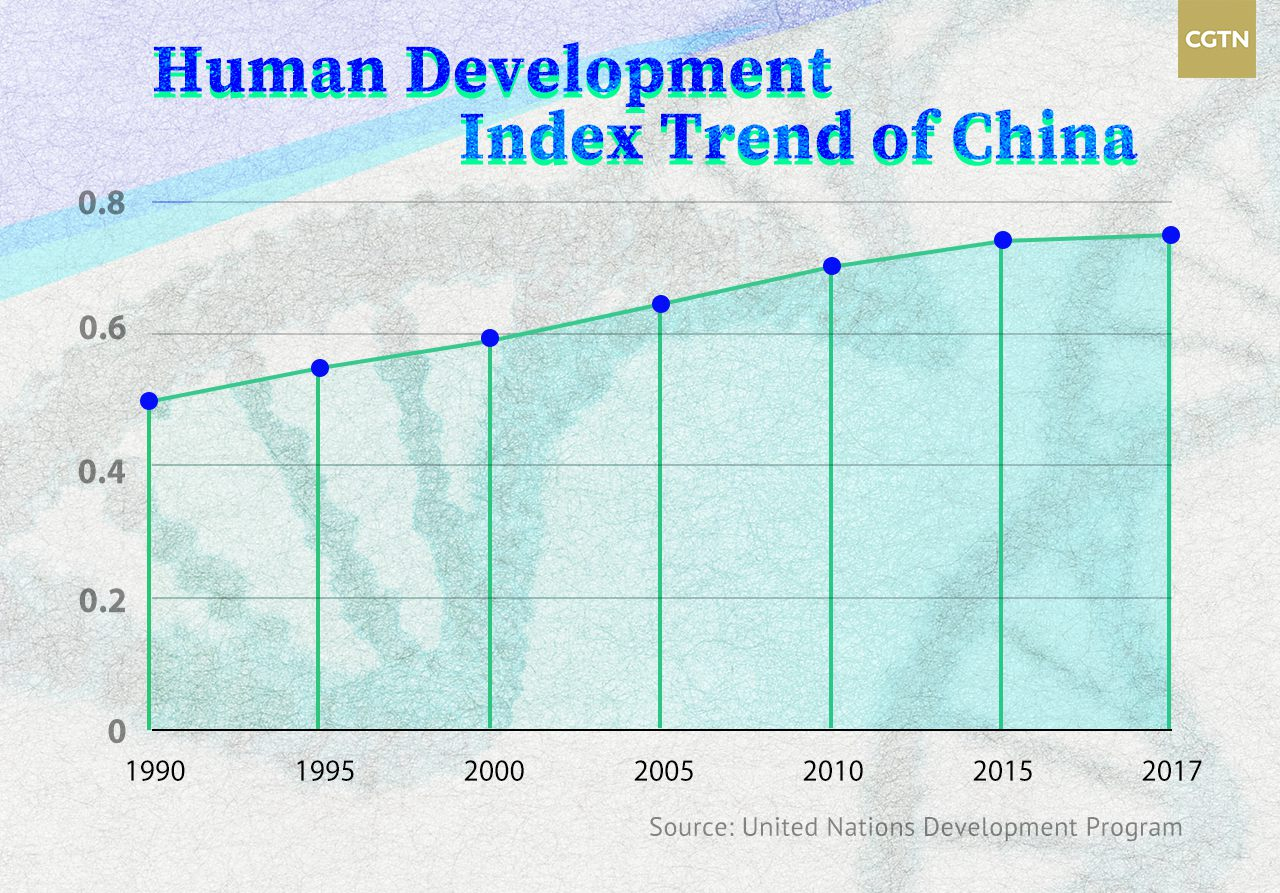
If we go by the above calculations, the HDI of China has been on the rise in the past 40 years. As of 2017, China's HDI scored to 0.752, ranking 86th on the United Nations Development Program.
CGTN Photo
CGTN Photo
In 2014, China became the only country since 1990 to emerge from a low-development level to high levels.
It is expected that the HDI of China may reach 0.902 by 2035. Even though problems such as aging population, and uneven access to education and health resources still exist, with a deepened reform and opening-up policy in place, the country is destined to achieve further in improving its human development.
(Infographics by Yin Yating)

SITEMAP
Copyright © 2018 CGTN. Beijing ICP prepared NO.16065310-3
Copyright © 2018 CGTN. Beijing ICP prepared NO.16065310-3