By CGTN's Wu Lei
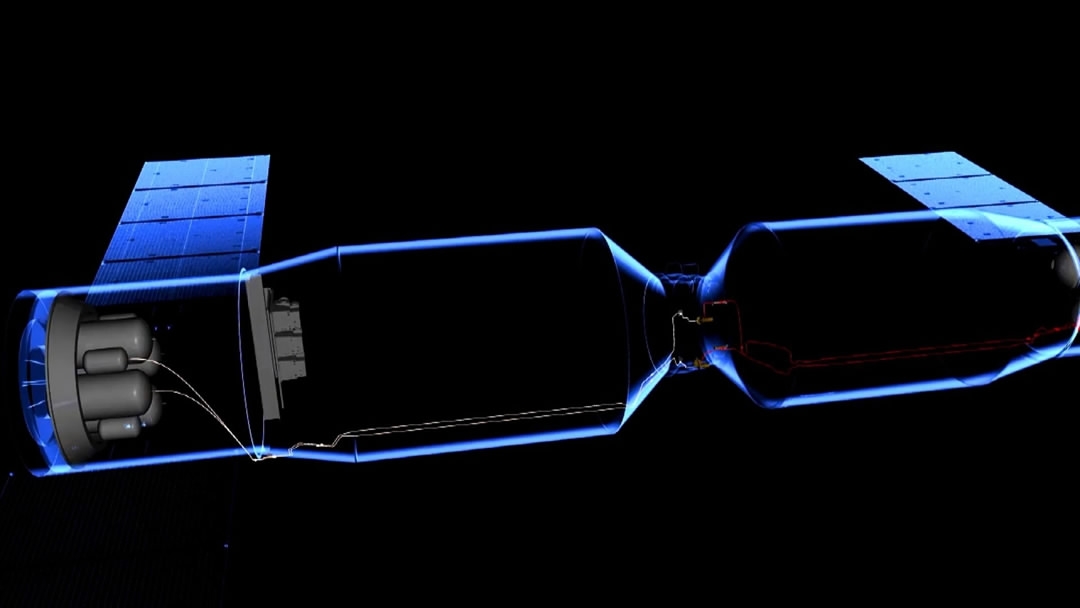
China’s cargo spacecraft Tianzhou-1 successfully docked with the Tiangong-2 space lab for the first time on Saturday, providing vital fresh propellant for the lab while in orbit. This is the first time that Chinese scientists have carried out a propellant refueling operation in space.
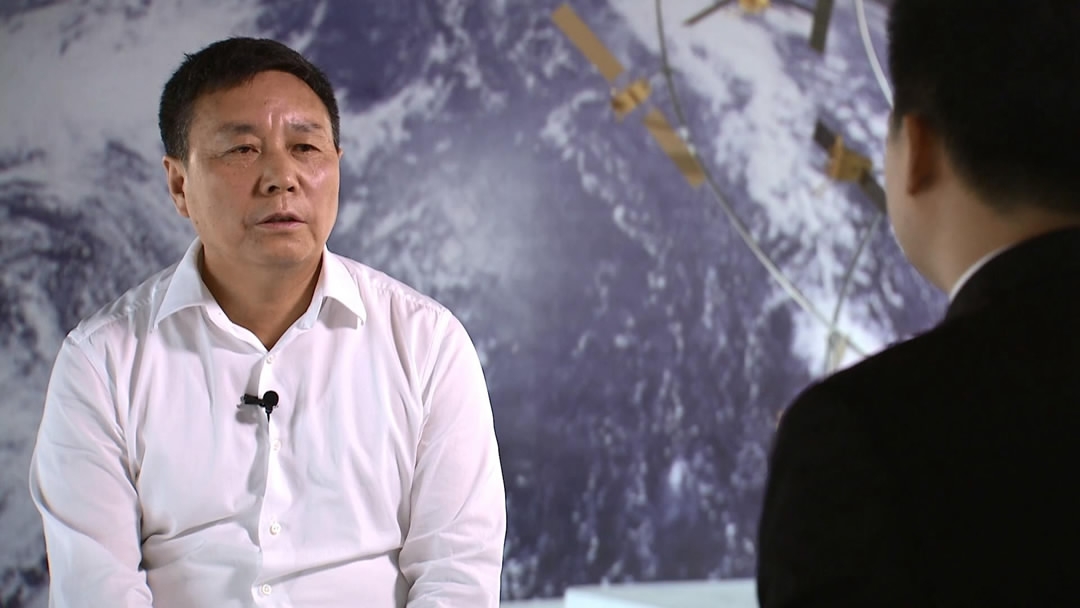

Wang Jianshe, of the China Academy of Aerospace Propulsion Technology said there are a lot of challenges during the refueling process. /CGTN Photo
Spacecraft are only able to bring a limited amount of propellant into space. After it is all gone, the spacecraft will no longer function. In order to extend a ship’s lifespan, the propellant can be topped up in orbit. There are many challenges in this process – for example, the docking technology, the recycling of high-pressure gas, and the refueling itself.
Contingency plans are in place in case of a propellant leak. /CGTN Photo
The engineers have fully considered contingency plans while designing the refueling system. In the event of a propellant leak during the refueling process, the system can locate and isolate the leak immediately, so the refueling can continue with minimal loss.
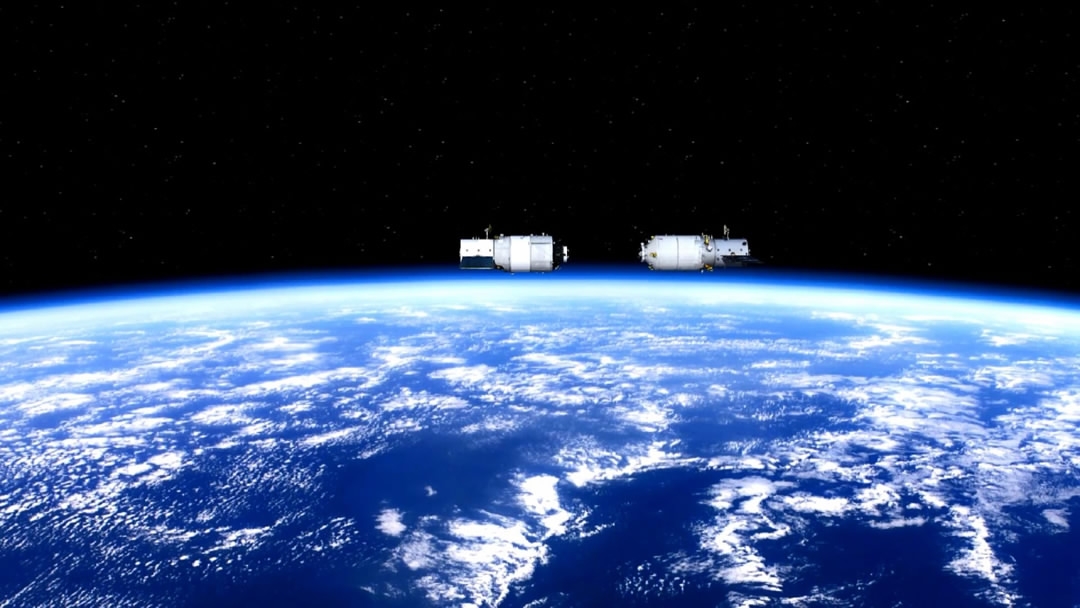

China will become the second country to master this cutting-edge technology after Russia. /CGTN Photo
The only other country with this refueling technology is Russia (the European Space Agency has conducted in-orbit propellant refueling, but it was reliant on Russian technology).
Wang Jianshe, of the China Academy of Aerospace Propulsion Technology, told CGTN the academy started designing and studying this system in 2005. It is completely self-developed technology that required a lot of technical breakthroughs.
Propellant refueling is a must for spacecraft's long term operation /CGTN Photo
China plans to build its own space station around the year 2022. There will be more spacecraft launched in the coming years. With this propellant refueling technology, these spacecraft will be able to stay longer in orbit and save some costs. Therefore, this technology is regarded as one of the most important steps towards China's goal of establishing its own space station. Only by doing this can the long-term operation of a future space station be guaranteed.