The life expectancy of people infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in Europe and the United States has been boosted by a decade since anti-AIDS drugs became available in the mid-1990s, researchers said on Thursday.
Microscopic view of HIV virus, cross section. /CFP Photo
A 20-year-old who began treatment at any time since 2008 now has an expected lifespan, about 78 years, approaching that of an uninfected person, said a study in The Lancet HIV. Life expectancy in the "general population", excluding people infected with the AIDS-causing virus, is 79 years for men and 85 for women in France, and 78 for men and 82 for women in the United States, said the researchers.
People who started antiretroviral treatment (ART) in 2008 or after lived longer, healthier lives than those who started treatment in earlier years, the researchers added. This was likely because modern drugs have fewer toxic side-effects, but are better at preventing the virus from replicating in the body. Newer drugs also have greater resistance to the virus.
Antiretroviral therapy combines three or more drugs which stop the HIV virus from progressing. /Science Photo Library
"With the perception that HIV-positive people will live into old age, clinicians are screening for and treating comorbidities (diseases on top of HIV) more aggressively," said the paper. These included heart disease, hepatitis C and cancer.
Conducted in Europe and America, the study included data on more than 88,000 HIV patients.
"Information about life expectancy in people living with HIV and the knowledge that it could be approaching that of the general population is important to motivate at-risk individuals to test for HIV and convince those infected to start ART immediately," said the study.
It could also "decrease stigmatisation of people living with HIV and help them to obtain insurance or employment."
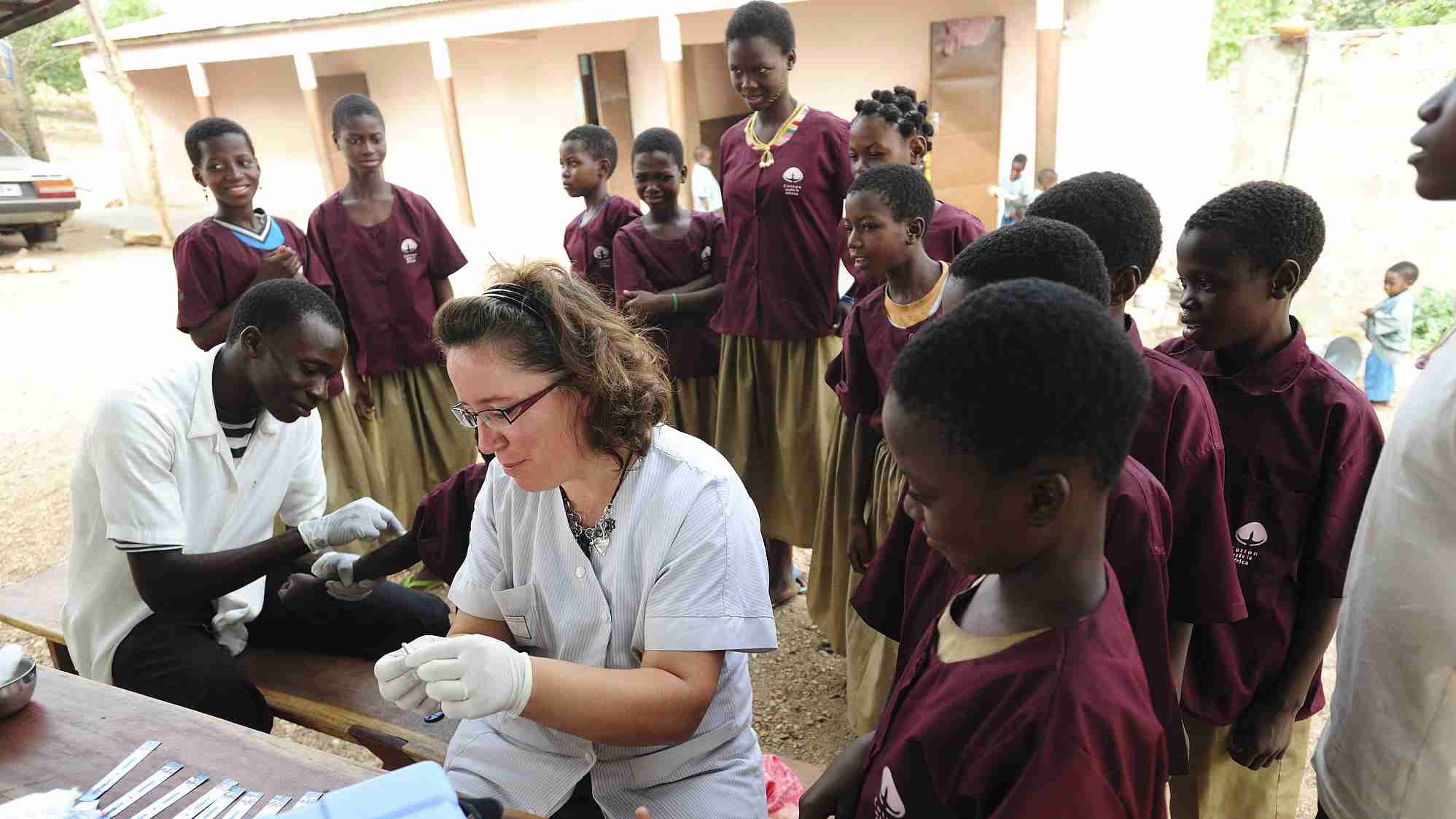

HIV quick test in a private orphanage in Natitingou, Benin. /CFP Photo
ART, involving a combination of three or more drugs that block the virus from replicating, first became widely used in 1996. It does not cure the disease, and treatment is lifelong. The World Health Organization recommends that ART be started by all people as soon as possible after diagnosis. Many people in poorer nations are diagnosed too late, if at all, and treatment is not always readily available or affordable.
(Source: AFP, BBC)