
China
23:11, 21-Jun-2017
Extreme heat grips Northern Hemisphere on summer solstice

Extreme heat across large tracts of the Northern Hemisphere raised fears for crops in China, fueled forest fires in Portugal and Russia's Far East, forced flight cancellations in the Southwest US, and melted tarmac on roads in Britain.
As Wednesday marked the summer solstice – the longest day of the year – forecasters said temperatures in Paris were expected to hit 37 Celsius (100 Fahrenheit), Madrid could see 38C, and London and Beijing was set for 34C and 33C with warnings of thunderstorms.
Rounding up the record temperatures set in the past two months, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) said the Earth was experiencing "another exceptionally warm year" and the heatwaves were unusually early.
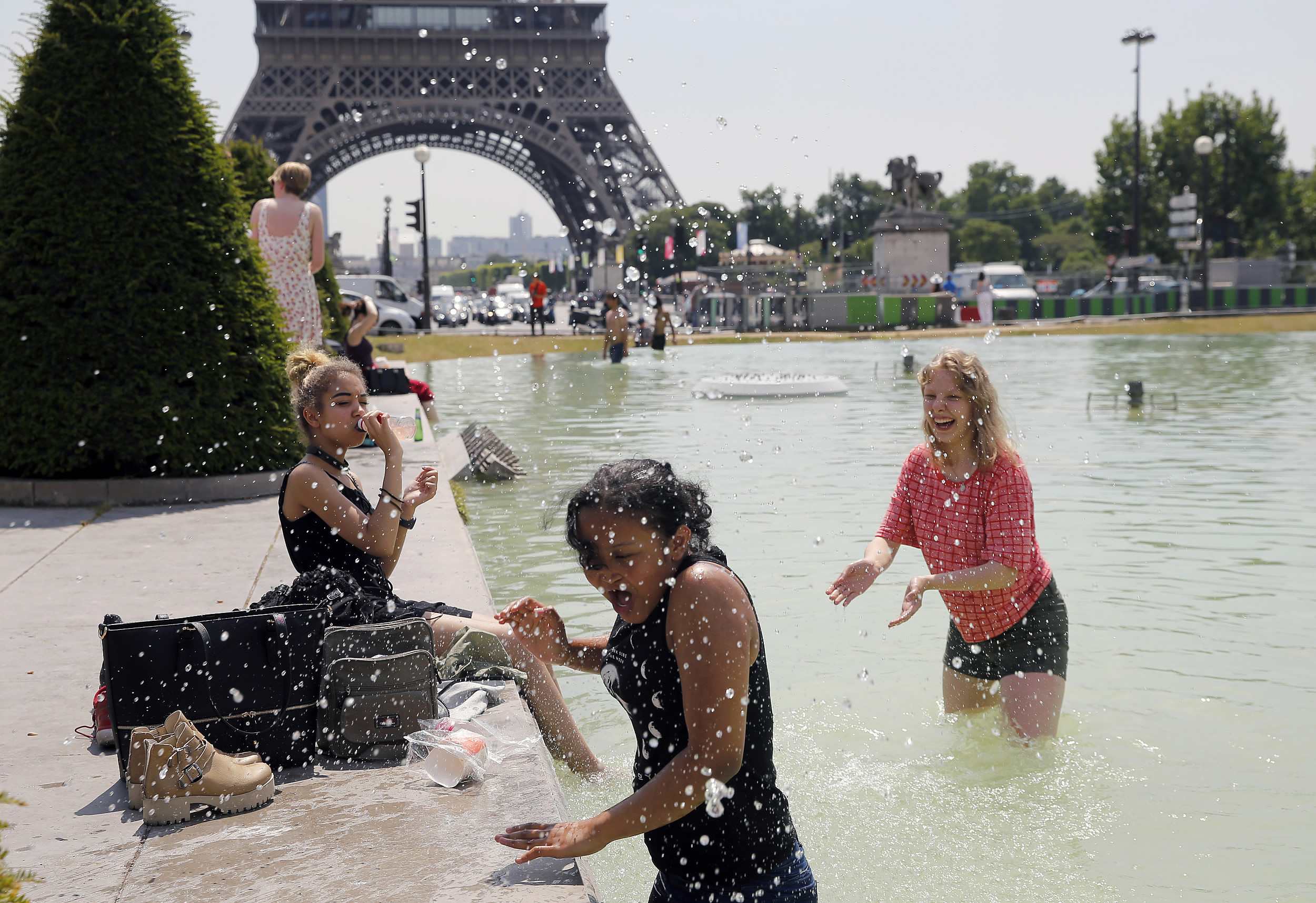
Parisians and tourists enjoy cooling down in the water of the fountain of the Trocadero next to the Eiffel Tower during the heat wave on June 20, 2017 in Paris, France. /VCG Photo
Parisians and tourists enjoy cooling down in the water of the fountain of the Trocadero next to the Eiffel Tower during the heat wave on June 20, 2017 in Paris, France. /VCG Photo
"Parts of Europe, the Middle East, North Africa and the United States of America have seen extremely high May and June temperatures, with a number of records broken," the WMO said late on Tuesday.
Even before this month, US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) data showed Europe, the United States and Northeast Asia - including eastern China, Japan and South Korea - had experienced unusually warm weather between March and May.
In China, the world’s top grain producer, hot and dry conditions in the main corn belt have delayed plantings and stunted crop development, especially in the province of Liaoning where soil moisture levels are at their lowest in at least five years.

Farmers tend to crops under hot weather in east China's Zaozhuang in Shandong Province. /VCG Photo
Farmers tend to crops under hot weather in east China's Zaozhuang in Shandong Province. /VCG Photo
Thomson Reuters Eikon data shows that precipitation in Liaoning for the past month has been between 40 and 60 percent below the seasonal norm.
"The drought that hit parts of China’s northeast is the worst for this time of the year in the past decade, in the breadth of areas it has affected and the length of time it has lasted," Ma Wenfeng, analyst at Beijing Orient Agribusiness Consultancy, said.
The hot, dry weather is a major factor behind forest fires that have killed dozens of people in Portugal, while the Russian news agency Tass reported scores of forest fires, mostly in Siberia and the far east region of Irkutsk.

VCG Photo
VCG Photo
In the US Southwest, flights were canceled mostly by regional airlines whose aircraft operate at a lower maximum temperature.
And in Britain, regional media in the southeast county of Surrey reported that the intense sun had melted tarmac roads.
Firefighters were on alert in Austria, where revelers were set to mark the solstice by setting light to hundreds of bonfires to celebrate the festival of Saint John – a tradition that goes on until the end of the month. Local authorities also announced a ban on barbecues in public parks, another popular tradition, to reduce the fire risk.

People in southwest China's Chongqing play in water. /VCG Photo
People in southwest China's Chongqing play in water. /VCG Photo
The Climate Change Institute at the University of Maine recorded temperatures in the Northern Hemisphere were 0.44C (0.8F) above the norm on Tuesday, compared with a global average of 0.25C above usual.
A study published earlier this week found that nearly one in three of the world's people were already exposed to potentially deadly heatwaves and predicted that number would rise to nearly half by the end of the century unless governments take steps to aggressively reduce climate-changing emissions.
"People are talking about the future when it comes to climate change, but what we found from this paper is that this is already happening … and this is obviously going to get a lot worse," said Camilo Mora, geography professor at the University of Hawaii at Manoa and lead author of the study published in the Nature Climate Change journal.
(Source: Reuters, AFP)

SITEMAP
Copyright © 2018 CGTN. Beijing ICP prepared NO.16065310-3
Copyright © 2018 CGTN. Beijing ICP prepared NO.16065310-3