
Having traveled about 475 million kilometers from Earth, China's Tianwen-1 spacecraft finally entered orbit around Mars on Wednesday.
The probe, consisting of an orbiter, a lander and a rover, activated its braking engines at 19:52 BJT. After reducing the speed for about 15 minutes, the Tianwen-1 has been captured by Mars' gravity and entered into a long elliptical orbit, according to the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC).
The successful brake enabled the Tianwen-1 to continue its Mars journey in the following months before making a final landing on the Red Planet.
The latest maneuver, also known as Mars orbit insertion, performed by the Tianwen-1, marks a decisive moment during the whole mission. Whether the spacecraft can continue its exploration and get first-hand data from Mars depends entirely on this step.
In the past couple of months, researchers have tweaked the probe's trajectory to Mars for four times to make sure it can reach the right orbit at the appropriate time.
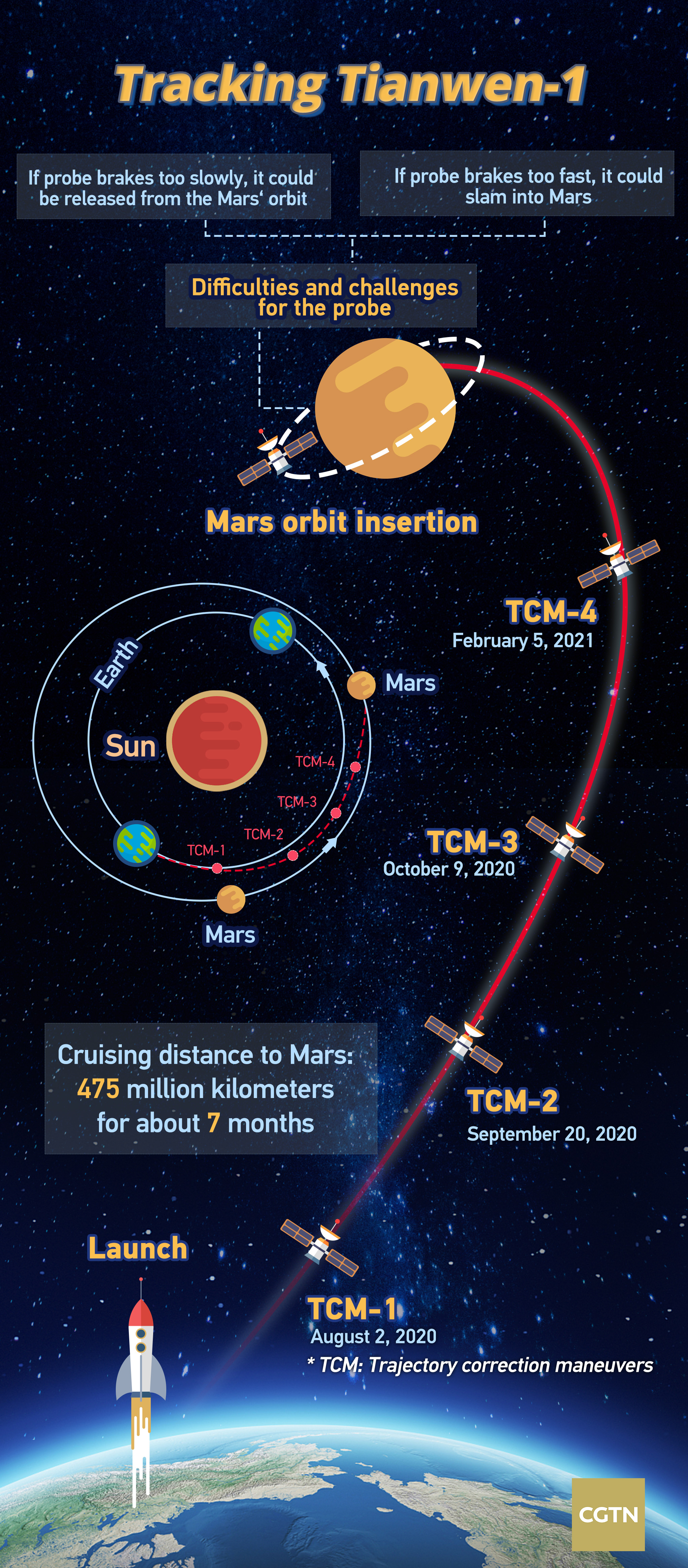
"Entering the Mars' orbit is a one-shot kill and has no room for failure," said Yang Yuguang, a researcher at the CASC, adding the timing, speed, and distance have to be precisely calculated.
The probe has to be slowed down to a certain speed before approaching the orbit. If the probe brakes too fast, it could crash on Mars, and if it brakes too slowly, it could skip Mars, according to Yang.
What's more, signal transmission is delayed due to the probe's long distance from Earth. It has to perform maneuvers on its own in response to the delay, making this step even harder to complete.
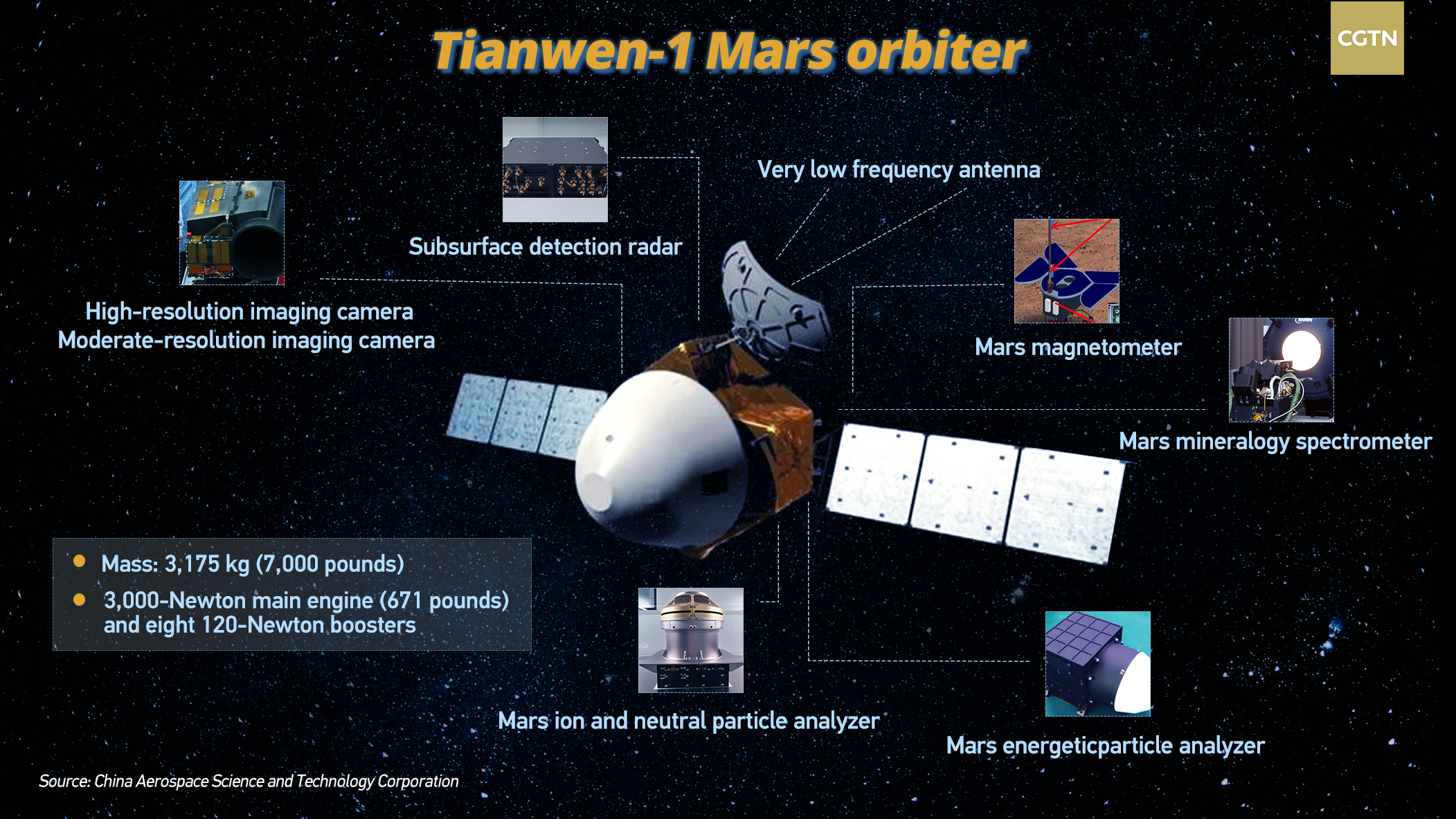
The journey to Mars has taken about seven months. After entering Mars' orbit, the Tianwen-1 will spend two to three months surveying potential landing sites using a high-resolution camera on the orbiter and make preparation for the landing in May.
After landing, a rover will be released to conduct scientific exploration with an expected lifespan of at least 90 Martian days (about three months on Earth), and the orbiter, with a design life of one Martian year (about 687 days on Earth), will relay communications for the rover while conducting its scientific detection.
The Tianwen-1 is one of the three missions targeting the Red Planet this month. On Tuesday night, the United Arab Emirates became the fifth nation in history to reach Mars after its Hope spacecraft entered the orbit. NASA's Mars rover Perseverance is also scheduled to make a soft landing on Mars' surface on February 18.
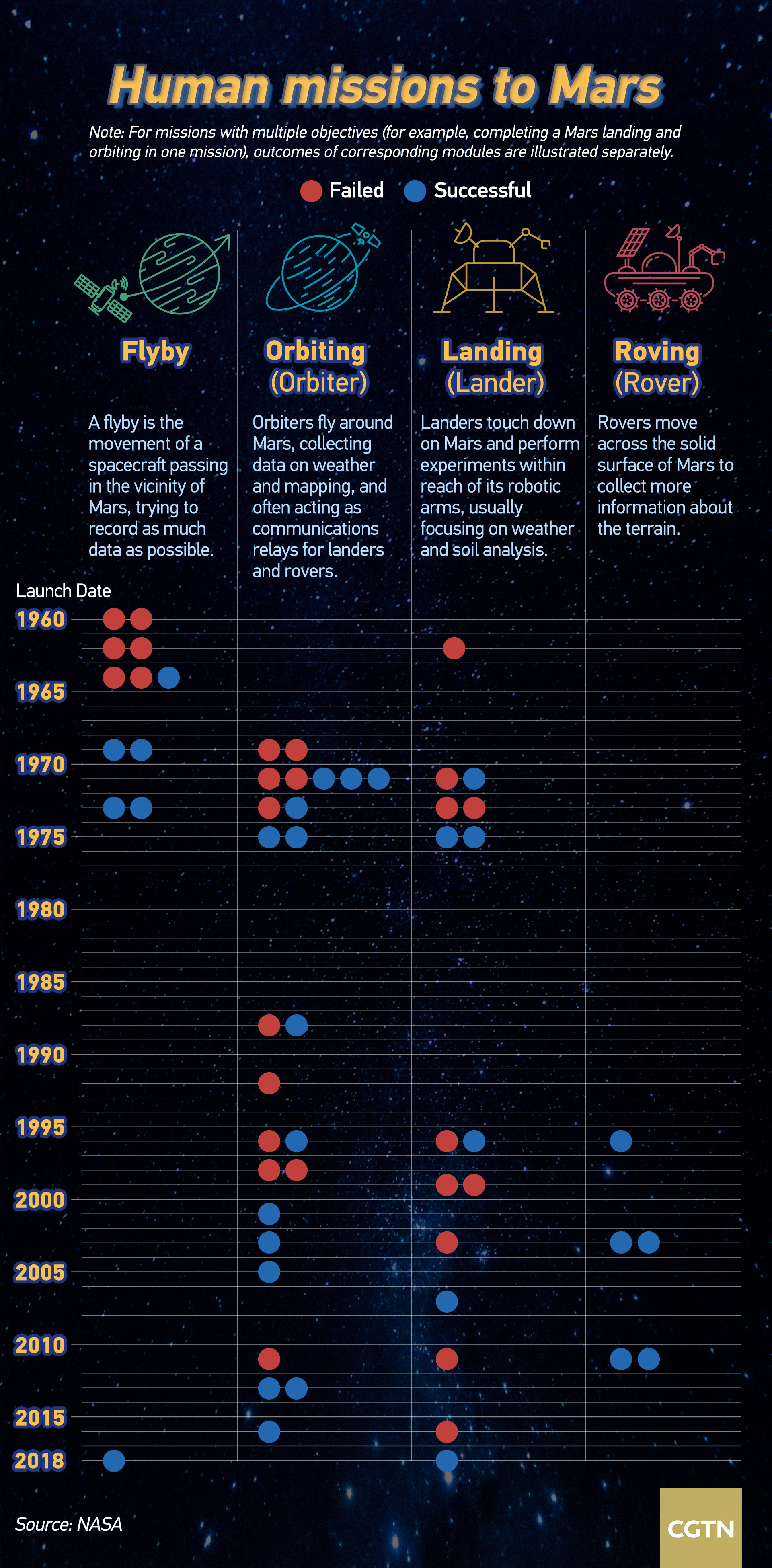
In the solar system, Mars is the closest planet to Earth and has some similarities to our natural environment. The Red Planet has always been one of the most sought after destinations in humans' space adventures.
But exploration to Mars is not always rainbows and butterflies. Data shows half of the attempts to explore the planet failed. As a result, Mars has long been dubbed a "graveyard" for spacecraft.
(Graphics by CGTN's Du Chenxin, Chen Yuyang)

