02:59

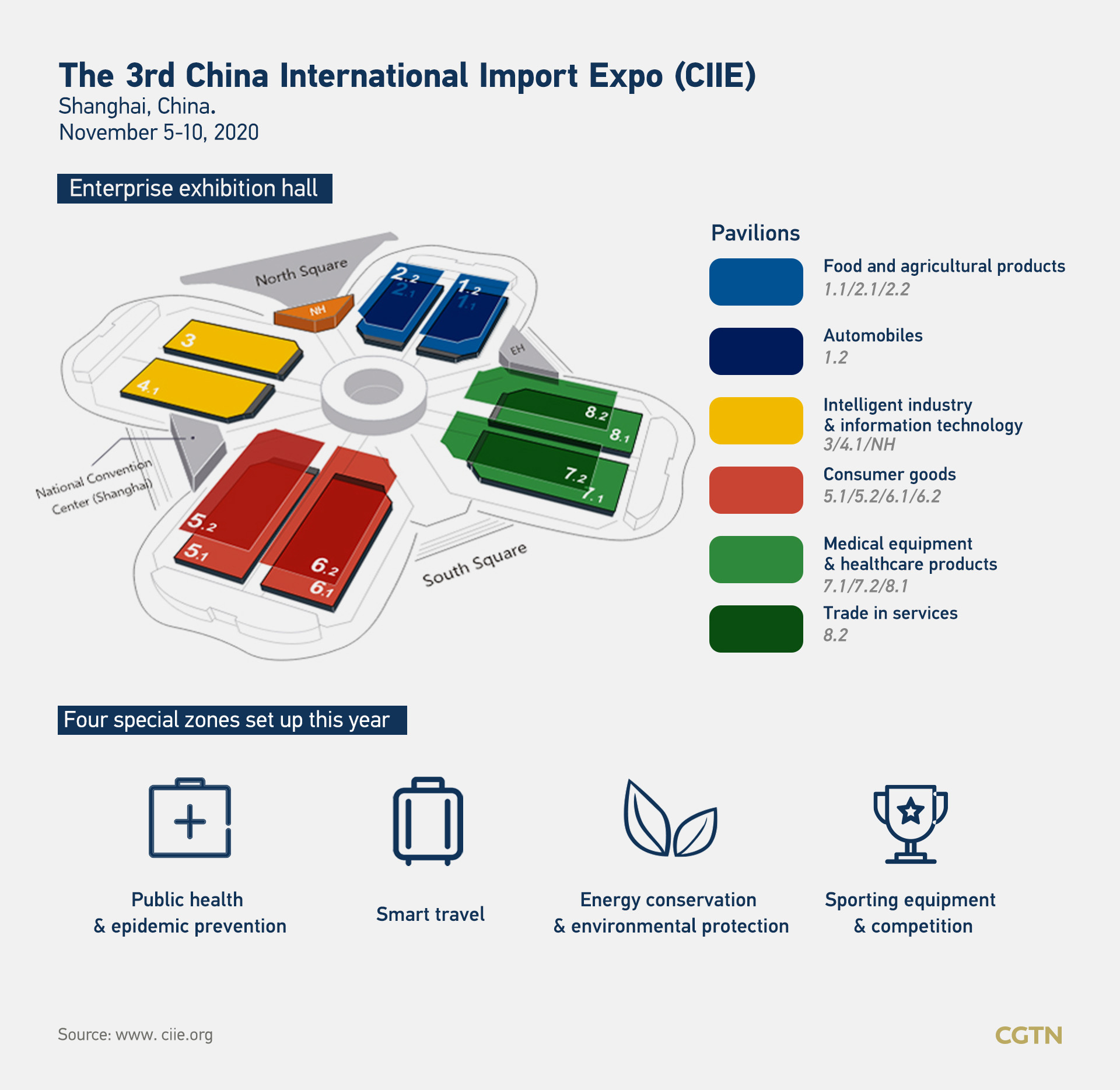
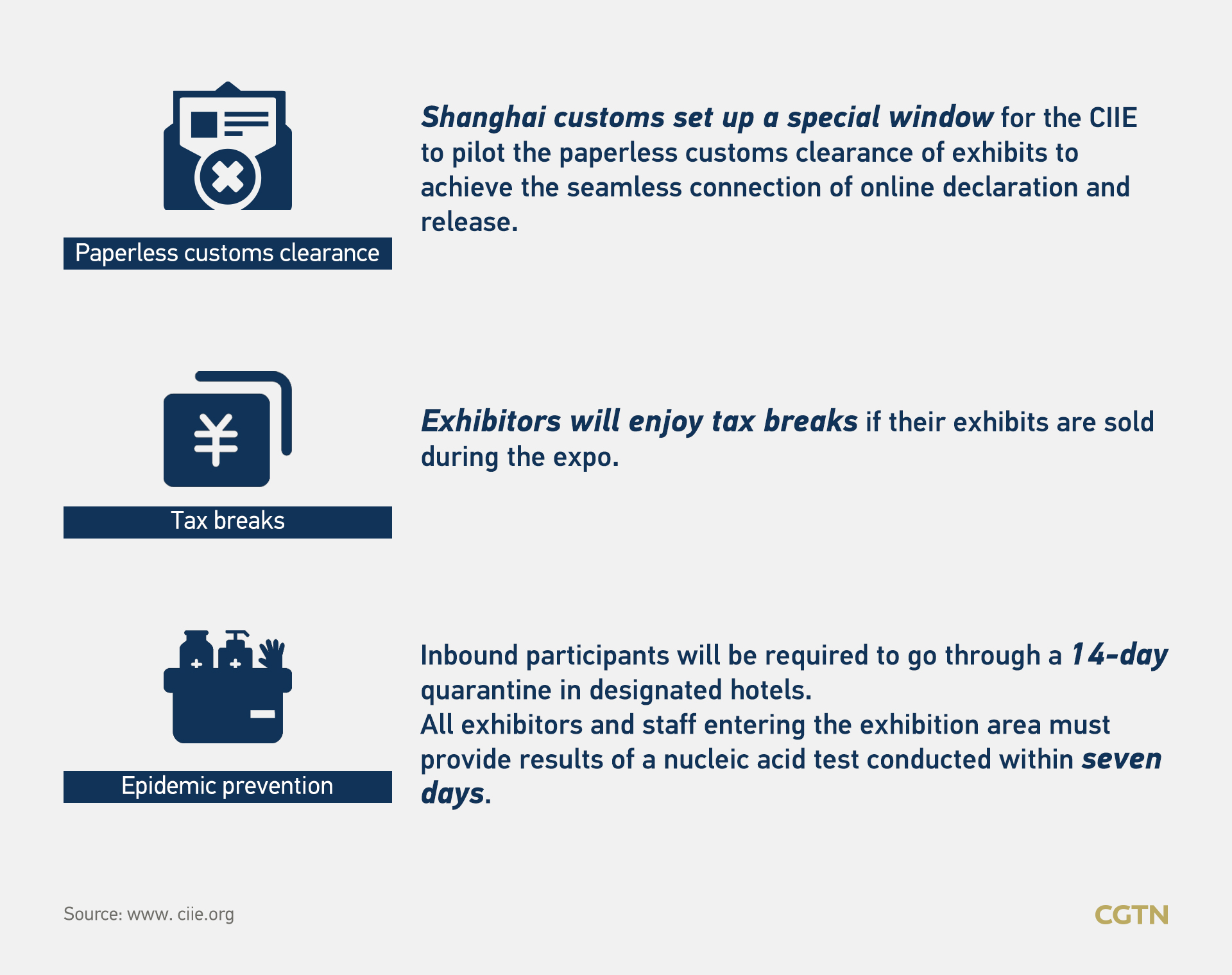
The third China International Import Expo (CIIE) is set to take place on schedule despite the COVID-19 pandemic. The six-day expo will start on Thursday in Shanghai.
Thanks to its effective pandemic control measures, China has made the swiftest recovery from the pandemic among major economies. In the first three quarters, its economy expanded by 0.7 percent from a year earlier, while the rest of the world is still largely mired in recession. The country's total imports and exports also recorded positive year-on-year growth in the same period.
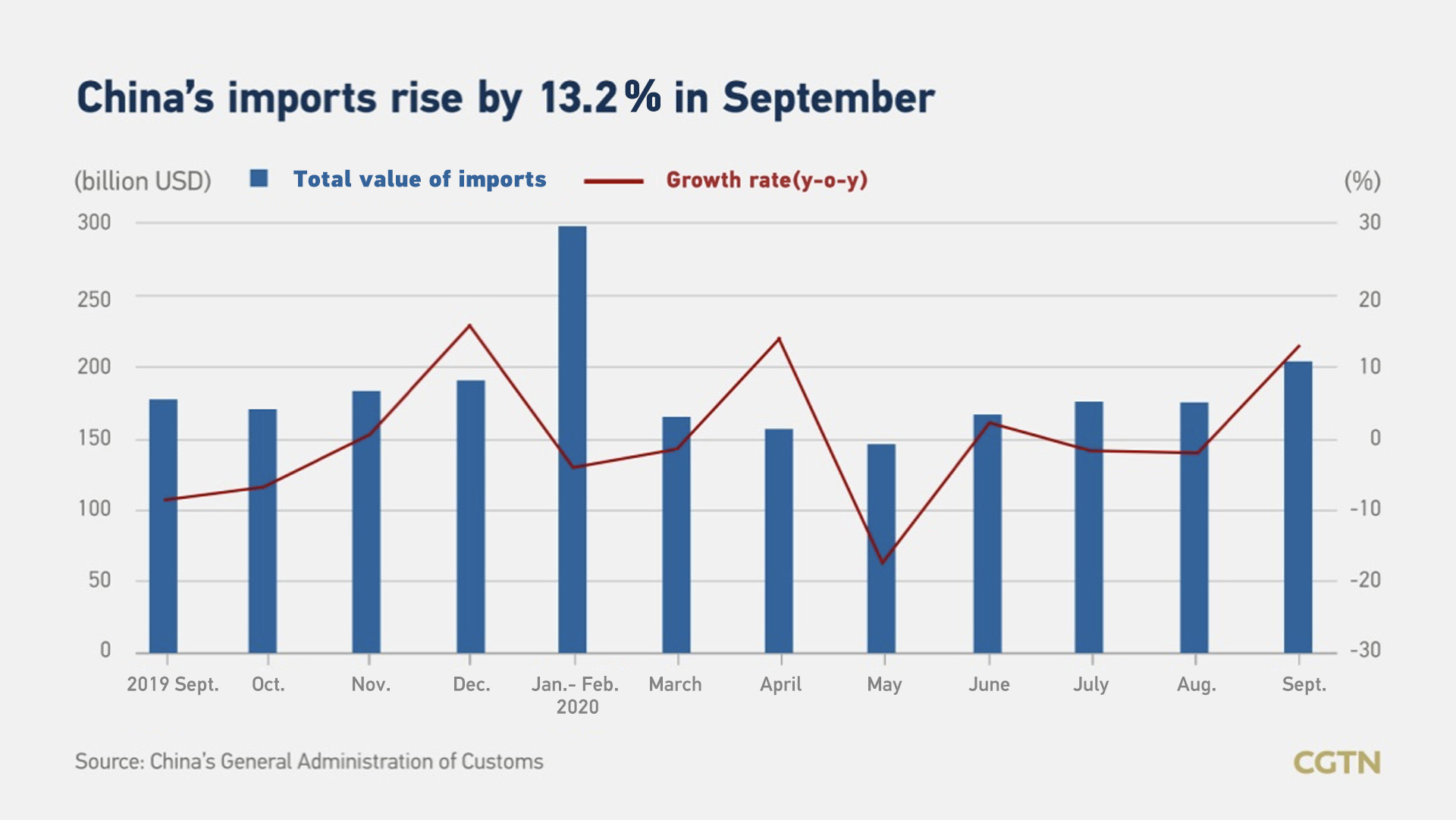
China's imports surged by 13.2 percent year on year in September, recording the fourth successive expansion. The country's import strength is lifting economic activities in neighboring countries, like South Korea and Japan, which have both seen a jump in exports to China in the September quarter.
China has made strenuous efforts to restructure the export framework since the 2008 financial crisis by increasing the added value in the final product and progressively embracing green growth.
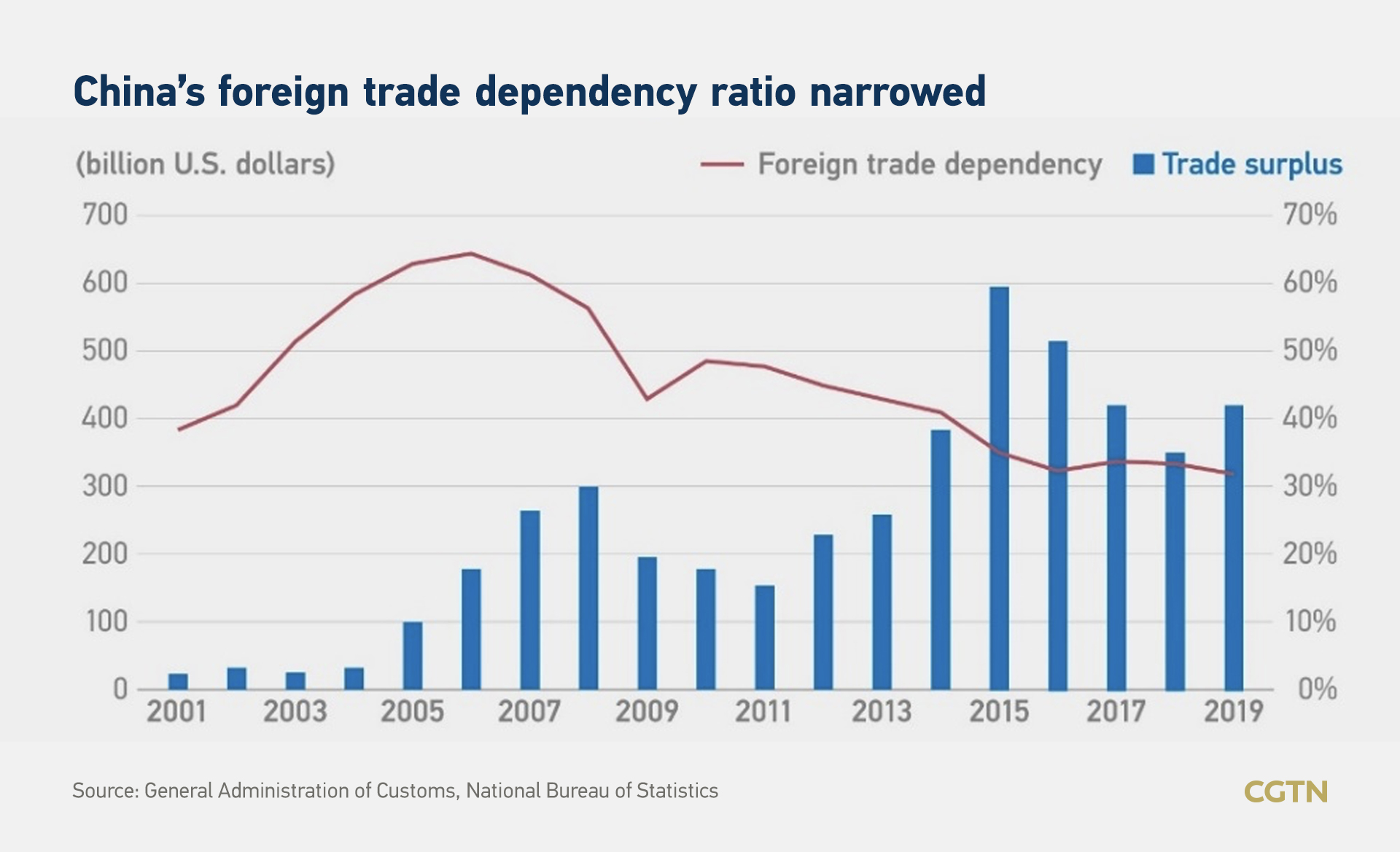
The country has also put forward a strategy to expand domestic demand. China's foreign trade dependency ratio, which measures the total amount of foreign trade to its GDP, has also been halved to just over 30 percent in the last two decades.
The world's second-largest economy has been promoting a "dual circulation" development pattern since May. The strategy indicates an economic development pattern that takes domestic development as the mainstay, with domestic and international development reinforcing each other.
Consumption power
China has a growing domestic market with a per capita GDP of $10,000, a tenfold growth in 20 years. From 2014 to 2019, consumption was the biggest contributor to economic growth, accounting for 58 percent of the country's GDP growth in 2019.
China has implied that its "dual circulation" plan is a long-term strategy to sustain growth amid the COVID-19 pandemic and rising unilateralism in the global economy.
Domestic circulation, which focuses on domestic demand, aims to promote the upgrade of the supply-side structure and strengthen the economy's resilience.
The pattern also aims to energize international circulation, as China has vowed to continue to expand opening-up and improve efficiency through external competition.